ProtoMAX®
Operation Guide
|
OMAX Corporation |
|
Information:
|
info@protomax.com |
This document contains subject matter to which OMAX® Corporation has proprietary rights. Recipients of this document shall not duplicate, use, or disclose information contained herein, in whole or in part, for any use other than the purpose for which this manual was provided.
OMAX Corporation believes the information described in this manual is accurate and reliable. From time to time, design improvements will be made to the OMAX equipment. Photographs, text, and sketches within the body of this manual may not exactly represent your equipment. In general, this manual contains the most up-to-date information available. However, OMAX Corporation cannot accept any responsibility, financial or otherwise, for any consequences arising out of the use of this material. The information contained herein is subject to change, and revisions may be issued to advise of such changes or additions. OMAX strives to continually improve user documentation. If you have any questions or concerns about the content of this user’s guide, please e-mail us at tech_writing@omax.com, or contact us by mail at:
OMAX Corporation
Technical Publications
21409 72nd Avenue South
Kent, WA, USA 98032
OMAX Corporation is continually improving their equipment to bring you the best in abrasive waterjet machining technology. For that reason, your abrasive waterjet may differ slightly from what is described in this document. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us at 1-800-298-4036 or e-mail us at info@protomax.com. You can also receive technical support on-line at: Web: http://www.protomax.com.
Original Instructions in English
April 2018
© 2018 OMAX Corporation
Important Safety Information
SAFETY IS YOUR RESPONSIBILITY.
For your own safety, read this guide thoroughly and carefully before the equipment is installed, operated, maintained, or issues are troubleshooted.
Save these instructions.
This guide contains important safety information for the equipment. Careful compliance with the safety information helps prevent physical injury, damage to the equipment, and can extend the equipment's life.
Equipment safety features, safety glasses, hearing protection, and more can reduce potential injury. Be careful when the equipment is installed, operated, and maintained. Safety guards and features do not guarantee your safety if you are careless, inattentive, or use poor judgment. If it feels dangerous, do not try it.
YOU ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR YOUR SAFETY IN YOUR SHOP.
Machine Safety Labels
These safety labels can appear on the equipment. If ignored, physical injury, death, or equipment damage may occur. Read the complete safety information in the operation, installation, or maintenance guide before the equipment is installed, operated, or maintained.

WARNING Electrical Shock
Dangerous voltages. Do not access areas with this label before the applicable safety precautions are done; lockout/tagout the power and make sure there is no voltage on the circuits before installation, maintenance, or other work is done.

WARNING Airborne Debris
Eye protection and hearing protection are required during operation. Do not remove the abrasive feed tube from the nozzle or hopper when pressurized. The pressure can blow abrasive into the air, and the abrasive particles can get into the eyes and contaminate tools and machines.

WARNING Keep Fingers and Hands Away From Parts that Move
Keep hands and fingers away from the machine when it moves and during operation. Fingers and hands can be crushed and cut by machine parts when they move. Do not try to gain access to the machine or parts during operation.

WARNING Pinch Risk
Keep hands away from the edge of the catcher tank when the lid is closed.

WARNING Keep Hands Away From Jet
Do not put hands or fingers near the nozzle during operation. Immediately get medical aid for abrasive waterjet injuries. Injuries caused by high-pressure abrasive waterjet systems are dangerous. Do not wait to get medical aid!

WARNING Watch Hands and Fingers
Always keep the motor guards in position during operation. Keep hands away from belts and pulleys during maintenance and service.

Electrostatic Discharge
Attention! Be careful when electrostatic-sensitive devices are touched. Use electrostatic discharge protection procedures.

No Open Flame
Do not smoke near the equipment. Do not operate the equipment in an explosive atmosphere. Make sure ignition sources (such as flames or electrostatic discharge) are not near the equipment. Do not store flammable materials near the equipment. Do not use equipment in or around flammable gases or liquids. Do not let explosive or flammable vapors collect in the area around the equipment. Make sure there is good airflow in the work area to dissipate gases, vapors, and fumes. Be especially careful when machining materials that create sparks, such as titanium, which can cause gases in the catcher tank to explode.

Do Not Operate With Guard Removed
Do not operate when the guards or panels are removed.

Do Not Spray
Do not spray water on or near the machine's electrical enclosure.

Do Not Step
Do not step, stand, or walk on the slats. The slats can become weak after operations and can fall under more weight.

Read Manual First/Do Not Adjust
Do not adjust. Read the manual. Special instructions could be required before adjustments are made. Adjustments to the equipment can have unwanted effects and cause injury or damage.

MANDATORY ACTION Disconnect Power
Always disconnect the primary power cord from the electrical source to isolate the machine from its electrical supply.

Read Manual
Read the equipment operation guide for important safety information and operation instructions. Do not operate this machine until all safety precautions and operation instructions are read and understood.

Wear Hearing Protection
Always wear hearing protection when near the equipment during operation. When operated above water, noise levels can exceed 70 dBA.

Wear Eye Protection
Always wear approved safety glasses when the abrasive waterjet system is operated. Other types of glasses do not give sufficient eye protection! The garnet abrasive is not a chemical irritant, but garnet can cause an eye injury like sand if it is not quickly flushed. Also, the catcher tank water can contain particles from the material or other chemical irritants. Have an eye-wash station near the work area if the abrasive spray gets into the eyes.
Read the product labels and refer to product Safety Data Sheets (SDS) to identify the properties and risks of chemical products and materials referenced in this document. Use good industrial hygiene, safety practices, and personal protective equipment identified in the SDS.

Wear Gloves
The catcher tank water can have dangerous bacteria in it. A small break in the skin can introduce the dangerous bacteria into a wound. Always wear protective gloves if there are cuts or wounds on the hands or fingers. When material is put on or removed from the slat bed, wear gloves that give protection against sharp metal edges.
Read the product labels and refer to product Safety Data Sheets (SDS) to identify the properties and risks of chemical products and materials referenced in this document. Use good industrial hygiene and safety practices. Use personal protective equipment as specified in the SDS.
Safety Precautions
Safety instructions must be followed when the equipment is installed, operated, or maintained. If ignored, death or physical injury can result, or damage can occur to the equipment. Always follow the applicable safety precautions when work is done with this equipment.
Use the equipment ONLY for its intended function
- Read the installation manual before the equipment is set up to learn about important installation and safety information.
- Read the documentation for recommended accessories. The use of incorrect accessories can cause a risk of injury to persons or damage to equipment.
- Wear eye and hearing protection. Always wear ISO-approved impact safety glasses.
- Make sure the equipment is installed correctly before the system is started.
- Never stand on the equipment. Serious injury can occur if the machine tips or you touch the machining tool during operation.
Do not make changes
- Do not make changes to the equipment or components that are not approved.
- Changes to the equipment can cause a risk of physical injury to the operator and others and can cause damage to the equipment or other property. Changes to the equipment will void the warranty.
- Do not change, defeat, or bypass the equipment safety features.
Do not remove panels
- Do not remove the panels during operation. Only remove them when required by maintenance or to troubleshoot problems.
Check for damaged parts
- Before the equipment is used, carefully examine guards or other parts that are damaged to make sure that it operates correctly and functions as intended. Examine to make sure parts that move, move freely, are aligned correctly, are not broken, are mounted correctly, and for other conditions that can have an effect on its operation. Replace guards or other damaged parts.
Use caution, stay alert, and be attentive
- Do not install, operate, or service the equipment while under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Read the warning labels on prescription and over-the-counter drugs. If in doubt, do not install or operate the machine.
- Do not install, operate, or service the equipment when you are tired.
- Always follow the safety precautions when the equipment is installed, operated, maintained, or serviced. Carefully operated, the abrasive waterjet is a safe tool. When operated carelessly, serious injury can result.
- Wear a face or dust mask.
- Do not reach over the machine to operate it. Keep feet on the floor and balanced at all times.
- Keep a minimum of 16 in. (40 cm) away from pressurized equipment during operation.
- Do not try to tighten the ultra high-pressure (UHP) fittings when the system is pressurized.
Keep the tools and equipment in good condition
- Keep machine and accessories clean for the best and safest performance.
- Always keep the equipment in good condition.
- Follow the maintenance instructions for equipment and accessories.
- Keep all protective guards and stop devices.
Keep the equipment and area around the equipment clean and free from clutter
- Remove all installation, operation, or maintenance tools from the equipment before it is operated.
- Keep the work area clean and clutter-free to prevent accidents.
- Keep the equipment clean for the best performance.
Do not operate the equipment in a dangerous environment
- Do not use the equipment in or around flammable gases or liquids.
- Do not expose the equipment to rain or use it outdoors.
- Keep the equipment in a bright work area.
Never leave the equipment unattended during operation
- Always stop and turn off the equipment before leaving the area.
- Keep visitors at a safe distance from the work area.
- Keep children away from the equipment work area.
- Do not let children play around or operate the equipment or its components.
Never operate the equipment without safety guards or covers
- Do not change, bypass, or try to defeat the safety guards, covers, or switches.
- Keep the guards in position and in working order.
- Do not remove the safety cover or guard during operation.
- Know the location of the ON/OFF switch.
- Know how to disconnect the primary power supply to the equipment.
- Start and operate the machine only when all side panels are in position.
Never put your hands in the area of the nozzle during operation
- Seek immediate medical aid for all waterjet injuries. Injuries caused by high-pressure abrasive waterjets are serious. Do not wait!
- Refer to the WaterJet Technology Association (WJTA) warning card for important medical aid information.

Figure 271
Be careful when material(s) is moved in the catcher tank
- Do not operate the equipment when material is moved into the catcher tank.
- Always stop the abrasive waterjet before adjustments are made to the material or the abrasive jet.
- Always be careful when material is moved into the catcher tank. Fingers can be caught between a heavy part and the support slats.
- Be careful around the support slats. The abrasive waterjet also cuts the support slats; the edges can become sharp and cause cuts or collapse.
Do not touch live electrical components or parts
- Always use a licensed electrician or approved person to install the primary power source to use with the machine.
- Examine the equipment power and control cables regularly for correct connection and installation. Damaged, exposed, and bare wires can cause electrocution or death!
- Make sure the equipment is correctly connected and grounded in accordance with the national, state, and local codes. Do not remove the prongs from the plug. Always plug into the correct electrical outlet.
- Never use any electrical plug adapter.
- Make sure the power switch is in the OFF position before the equipment is plugged in to stop accidental starts.
- Always disconnect the equipment from the primary power before service or maintenance work is done.
Noise Emission Precautions
Environmental factors, such as how the room or structure is built, other machines and power tools in the area, and other noise sources, can have an effect on the environment's true noise level. When installed and operated correctly, the equipment's A-weighted emission sound pressure level, LpA , is less than 75 dBA (LpA < 75 dBA). Therefore, OMAX recommends that the operator wear hearing protection during equipment operation.
Treat All Injuries with Caution
Injuries that involve contact with the catcher tank water should receive medical aid immediately. Refer to the WJTA Warning Card for important medical aid information.
Get medical aid immediately for an abrasive waterjet injury. Tell the physician the cause of the injury, the type of abrasive waterjet work that was done when the accident happened, and the water source.
Stagnant water in the catcher tank can introduce dangerous bacteria into cuts, scrapes, small breaks in the skin, and other types of wounds. Injuries that involve contact with the catcher tank water should receive aid immediately. Injuries that involve contact with the water should be attended to immediately.
Unusual infections with aerophilic microorganisms that occur at lower temperatures have been reported. These can be gram-negative pathogens, such as those found in sewage. Bacterial swabs and blood cultures may be helpful to assist a physician's diagnosis.
An injury caused by high-pressure waterjets can be dangerous. If there is a waterjet injury:
- Get medical aid immediately. Do not wait!
- Tell the physician of the cause of the injury.
- Tell the physician about the type of abrasive waterjet work done when the accident happened and the water source.
- Give this information to medical personnel:
This patient may be suffering from a waterjet injury. Evaluation and management should parallel that of a gunshot injury. The external manifestations of the injury cannot be used to predict the extent of internal damage. Initial management should include stabilization and a thorough neurovascular examination. X-rays can be used to assess subcutaneous air and foreign bodies distant from the site of injury. Injuries to the extremities can involve extensive nerve, muscle, vessel damage, and cause a distal compartment syndrome. Injuries to the torso can involve internal organ damage. Surgical consultation should be obtained. Aggressive irrigation and debridement is recommended. Surgical decompression and exploration may also be necessary. Angiographic studies are recommended pre-operatively if arterial injury is suspected. Bandages with a hygroscopic solution (MgSO4) and hyperbaric oxygen treatment have been used as adjunctive therapy to decrease pain, edema, and subcutaneous emphysema. Unusual infections with uncommon organisms in immunocompetent patients have been seen; the source of the water is important in deciding on initial, empiric antibiotic treatment, and broad-spectrum intravenous antibiotics should be administered. Cultures should be obtained.
Lockout/Tagout
Do standard practices and procedures to shutdown and stop the equipment, isolate it from its energy source(s), and prevent the release of potentially dangerous energy when maintenance and service work is done.
Equipment Grounding Requirements
- Make sure the equipment is correctly grounded in accordance with the national, state, and local codes. Do not remove the prongs from the plug. Always plug into the correct electrical outlet.
- The ground wire gives the electric current a path of least resistance to reduce the risk of electrical shock during a malfunction or breakdown. The machine has an electric cord with an equipment-grounding conductor (EGC) and a ground plug (United States, Canada, and Mexico only). The plug must be connected to a matching outlet that is correctly installed and grounded in accordance with all local codes and ordinances.
- Do not change the plug—if it does not fit the outlet, have the correct outlet installed by a qualified electrician.
- If the EGC is incorrectly connected, it can result in electric shock.
- Contact a qualified electrician or service personnel if the grounding instructions are not understood or if not sure if the equipment is correctly grounded.
- Do not use extension cords with the equipment.
- If the cord is damaged or worn, immediately replace it. Contact OMAX for replacement parts and instructions. The insulation of the EGC is covered with a green or green with yellow-striped surface. If replacement of the electric cord or plug is necessary, do not connect the equipment-grounding conductor to a live terminal. Refer to the equipment-specific wiring configuration.
- The equipment is intended to be used on a circuit with an outlet similar to the one shown (United States, Canada, and Mexico only):

Figure 272
- The grounding plug is similar to the one shown (United States, Canada and Mexico only):
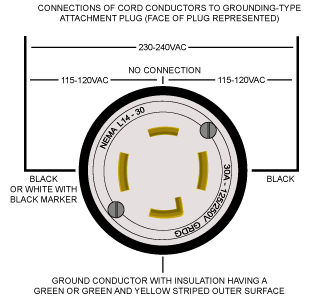
Figure 273
- Make sure that the equipment is connected to an outlet that matches the plug configuration.
- The equipment must not be connected to any different type of electric circuit.
- No adapter is available or should be used with this equipment.
- For countries other than the United States, Canada, and Mexico, OMAX does not supply a sufficiently rated industrial-grade plug.
- Contact a qualified electrician or service personnel to install a sufficiently rated industrial-grade plug in accordance with national, state, and local codes.
- A pin and sleeve plug, rated at least 30A, 230V, 2-pole+E (3-wire grounding), IP44 or better, having a first-make last-break protective bonding contact (earthing contact) in accordance with standards IEC 60309-1 and IEC60309-2 can fulfill this requirement.

Figure 274
- The cord must be plugged into a matching outlet that is correctly installed and grounded in accordance with all local codes and ordinances.

Figure 275
Explosive Atmosphere Precautions
Machining certain types of material, such as titanium, with a waterjet can cause sparks. Do not operate the equipment in an explosive environment. Do not let explosive or flammable vapors collect in the area of the equipment.
Removal of Waste Materials
Discard all machining wastes correctly in accordance with all local and federal regulations. Abrasive waterjet machining causes two types of waste: the water used for machining and the solid material that collects in the catcher tank. Although the used garnet abrasive is not dangerous, the waste deposited from the cut material can require special treatment.
In abrasive waterjet machining, high-pressure water with garnet abrasive particles hits and cuts the material. The abrasive grit and eroded particles from the cut material collect and settle at the bottom of the catcher tank until discarded. Different materials can have different requirements to discard them correctly. Always refer to all local and federal regulations. For example, when poisonous materials such as lead or radioactive metals are cut, the correct steps must be taken to discard the poisonous or radioactive water, material debris, and used abrasive garnet; local and federal regulations must be followed. Always refer to the local utility company for sewage or water treatment requirements and procedures to discard waste materials.
Sufficient Shop Ventilation
Make sure there is good airflow in the work area to dissipate gases, vapors, and fumes. The machine contains a large amount of water. The ambient temperature in the shop and of the water can have an effect on water evaporation. To decrease the effect on other equipment in the shop, make sure there is good airflow in the shop. Also, some materials, such as aluminum particles, are known to make hydrogen in water.
When aluminum is cut, the small particles of aluminum dust in the catcher tank react with the water to make flammable hydrogen gases. Usually, hydrogen bubbles to the surface and is released into the shop in safe, low concentrations.
Make sure no ignition sources (open flame or electrostatic discharge) are near the abrasive waterjet system.
Monitor the catcher tank for hydrogen gas bubbles when large quantities of aluminum are cut. The aluminum powder (made from the removed material) and spent garnet collect at the bottom of the catcher tank. The aluminum then reacts with the water and releases hydrogen gas. The hydrogen gas can collect in bubbles in the garnet. The hydrogen gas bubbles are flammable. Keep the garnet levels in the catcher tank low to prevent hydrogen gas bubbles from being collected within the garnet.
Do not smoke near the machine. Keep other sources of ignition or flammable materials near the machine. Be careful when materials that create sparks are cut, such as titanium, which can fire the gases in the catcher tank and cause an explosion. Remove the aluminum powder from the catcher tank before machining materials that spark.
Overpressure Protection
During operation, pump pressure is monitored to prevent an overpressure condition. If the pump pressure increases more than the factory-set maximum pressure limit, the safety relief valve starts and stops the pump.
Electrical Protection
The equipment controller includes short circuit, overcurrent, and thermal protection for the pump motor.
Electrical Disconnect/Emergency Machine Off (EMO)
An electrical disconnect/emergency machine off (EMO) switch is used to remove the primary AC electrical supply from the machine. To isolate the machine from its electrical supply, always unplug the primary AC supply power cord from its electrical supply outlet.
Safety Lid
The lid of the equipment has a safety interlock to prevent waterjet operation when the lid is open.
Safety Legend
The safety signal word panels and paragraph notifications can be shown throughout this and other documentation. Each gives the safety issue identification and recommended actions to prevent the risk. Be alert! Follow the recommended safety steps, procedures, and precautions to prevent injury or damage to the equipment.
Identifies a dangerous situation that could result in death or serious injury if not avoided.
Identifies a dangerous situation that could result in minor or moderate injury if not avoided.
Identifies situations that are important but not dangerous or related to physical injury; for example, messages related to property damage.
Used to give information, emphasize a point, or tips for easier operation.
Required Tools
The following table contains a list of tools with the appropriate sizes needed when operating the ProtoMAX.
Customer Provided Tools
These tools are not provided by OMAX or included with the ProtoMAX.
| Icon | Tool | Size(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Torque wrench | 15–102 in-lb (2–12 N·m) |
|
|
Hex socket | 4 mm |
|
|
Shop towels | |
|
|
Allen wrench | 4 mm |
|
|
Open-end wrench | 19 mm |
|
|
Crowfoot wrench | 19 mm |
OMAX Provided Tools
The following table contains a list of tools provided by OMAX that are needed to operate the ProtoMAX. Tools listed with part numbers are included with the ProtoMAX or are available for purchase. Contact technical support for more information.
| Icon | Tool | Size(s) |
|---|---|---|
|
Stand-off tool (P/N 317876) |
Technical Specifications
See ProtoMAX Utilities Requirements for the technical specifications.
Introduction
This guide provides information and instructions to operate the abrasive waterjet cutting system. It explains how the pump and abrasive waterjet system work. It also provides instructions on how to machine a part, how to start and stop the system, and how the software (Intelli-MAX® Proto) is used to machine a part.
Abrasive Waterjet Overview
The ProtoMAX abrasive waterjet is a precision machining tool that operates under software control using high-pressure water and garnet abrasive to cut complex parts out of most materials including metal, plastic, glass, ceramics, stone and composites using standard CAD drawing files.
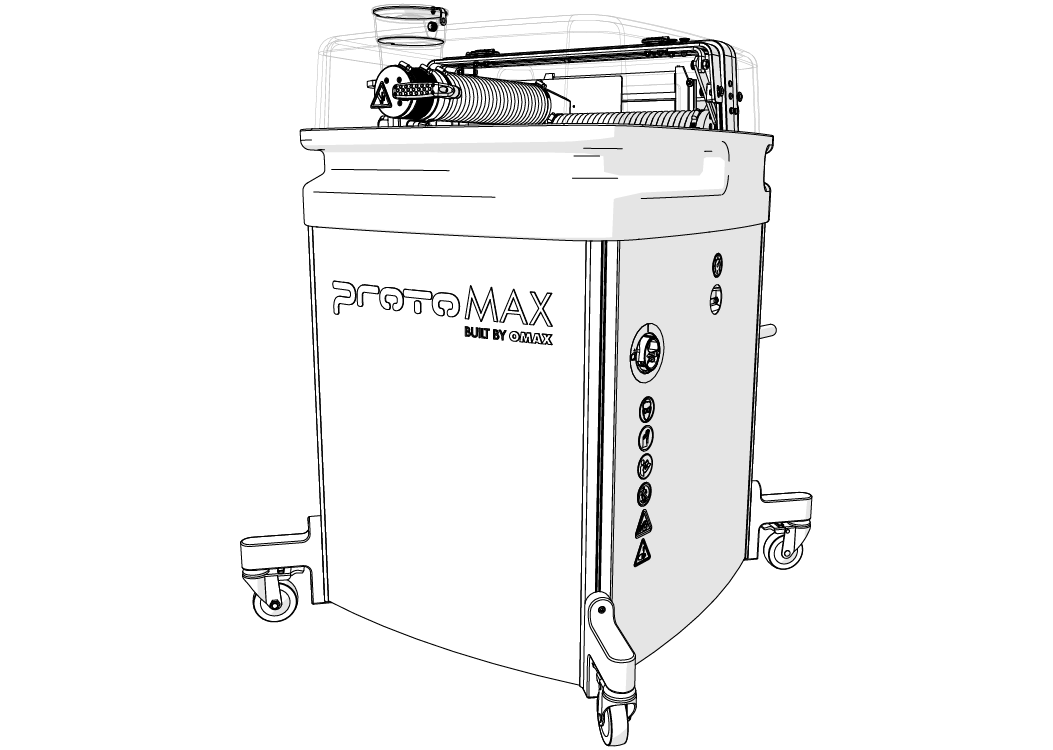
Components
The ProtoMAX takes up little shop floor space. The cutting stage has a 12 in. (30 cm) (X-axis) by 12 in. (30 cm) (Y-axis) cutting area with an easy material alignment system for cutting parts. The precision drive components are protected inside sealed bellows from water and garnet abrasive. The manual Z-axis allows cutting of materials up to 1 in. (3 cm) thick. The cutting area is fully enclosed by a see-through enclosure supporting a safety interlock system to halt abrasive waterjet cutting when opened.
The ProtoMAX consist of the following major components:
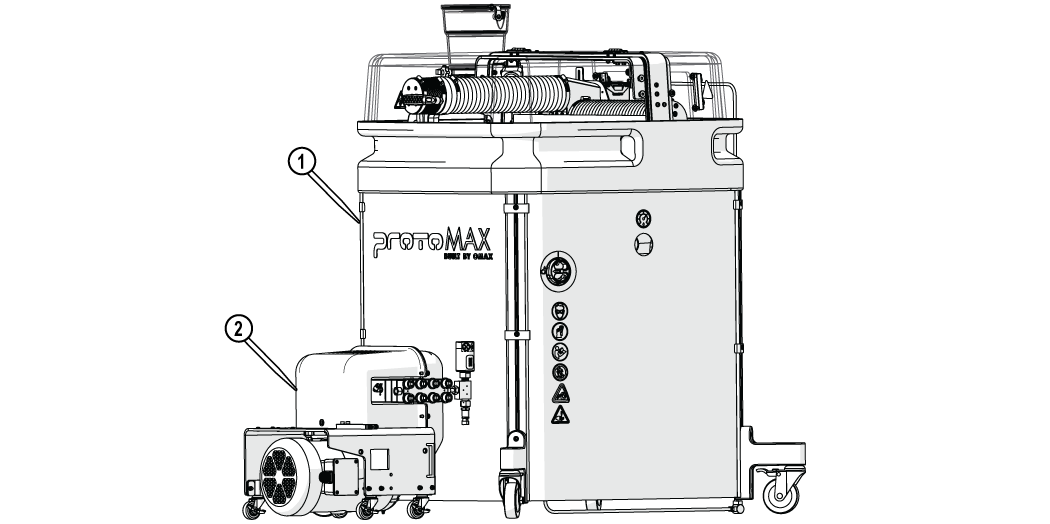
Figure 276
| [1] Table assembly | [2] High-pressure pump |
Table Assembly
The ProtoMAX table assembly is comprised of the cutting stage, garnet abrasive delivery system, catcher tank, electrical control enclosure, water filter, and operator controls.
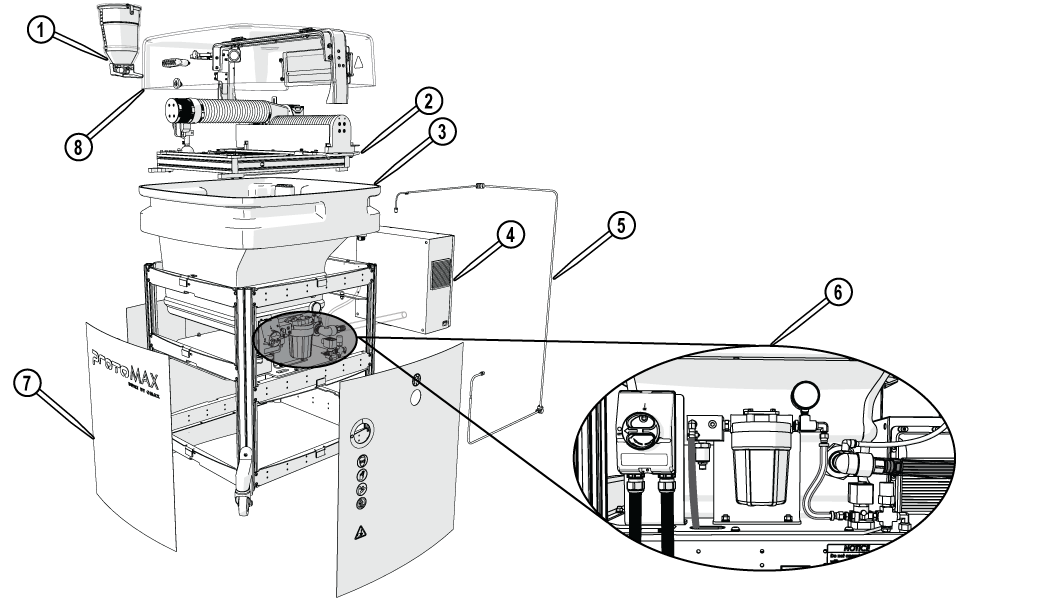
Figure 277
| [1] Garnet abrasive delivery system | [4] Electrical control enclosure | [7] Side panels |
| [2] Cutting stage and X, Y, and Z stage | [5] High-pressure plumbing | [8] Cutting stage lid |
| [3] Catcher Tank | [6] Power and water controls |
Cutting Stage Lid and Side Panels
Do not remove the side panels under normal conditions. Damage may occur when operating the ProtoMAX with the side panels removed. Only remove them when required by maintenance or troubleshooting procedures.
The cutting stage lid provides safe access to view the cutting process. The lid has a built in safety interlock switch that halts all cutting operations (pauses MAKE, stops stage motion, and turns off the pump) when the lid is opened. Always use the Pause button in the software to pause the system before opening the lid. This allows the operator to safely inspect the work and adjust materials as needed. Once the lid is closed, the cutting operation may be continued. Side panels provide protection to the catcher tank and pump. Incoming water pressure may be monitored through the viewing portal located on the right side panel. Panels should remain on the table assembly during operation. Panels can be easily removed for access to the interior components.
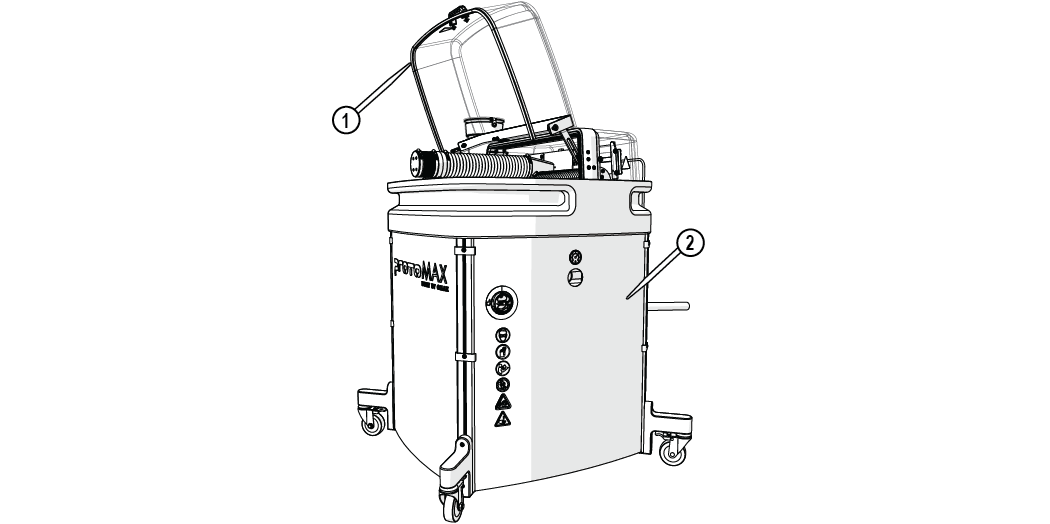
Figure 278
| [1] Cutting stage lid | [2] Side panel (x 3) |
X, Y, and Z-axis Cutting Stage
The cutting stage provides a 12 in. (30 cm) (X-axis) by 12 in. (30 cm) (Y-axis) cutting envelope. The Z-axis allows manual up and down movements for cutting materials up to 1 in. (3 cm) thick.
The cutting stage uses the same grid and coordinate system as in the Intelli-MAX software. When looking down on the table, the X-axis runs left to right and the Y-axis runs front to back. The Z-axis allows vertical movement of the cutting head. When the ProtoMAX is homed, the nozzle is moved to the position X=0 and Y=0 coordinate at the lower left corner of the cutting envelope.
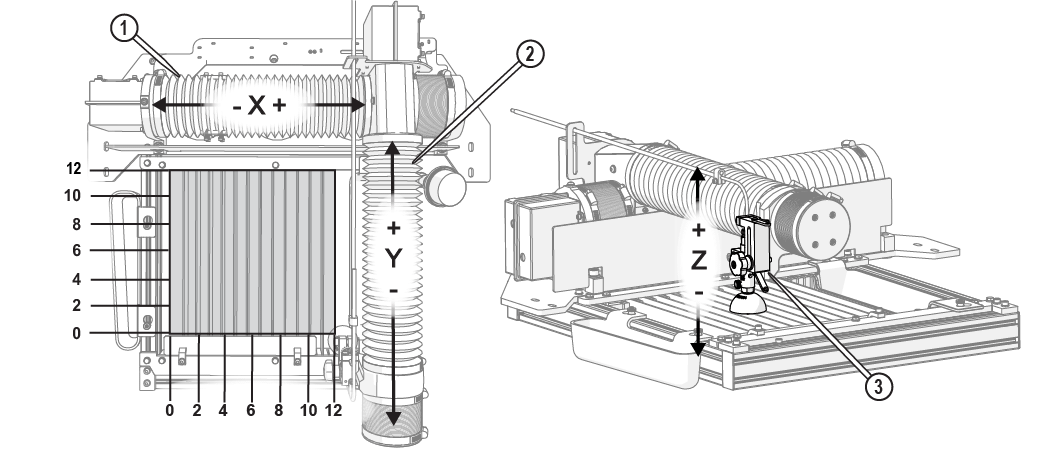
Figure 279
| [1] X-axis | [2] Y-axis | [3] Z-axis |
Slat Bed
The cutting stage has a removable slat bed assembly to support cutting materials. The slat bed assembly is removed to access the cutting tank for cleaning and maintenance. The slat bed assembly is secured to the cutting stage frame and provides support for the part being machined.
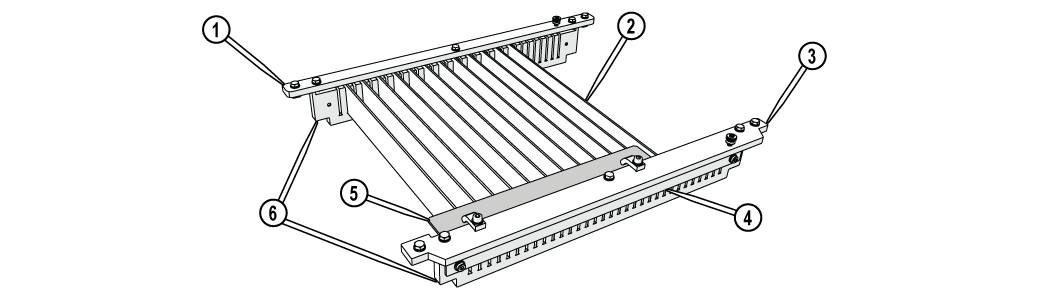
Figure 280
| [1] Mounting plate, rear | [3] Mounting plate, front | [5] Square fixture plate |
| [2] Slats | [4] Slat comb bracket (x 2) | [6] Slat comb (x 2) |
Catcher Tank
The catcher tank stores the water from the cutting nozzle and provides a settling tank for the spent garnet abrasive and cut away material. The catcher tank bottom is shielded to prevent cutting through when operating the machine.
Do not add chemicals to the catcher tank water. Damage to the catcher tank and other components may occur.
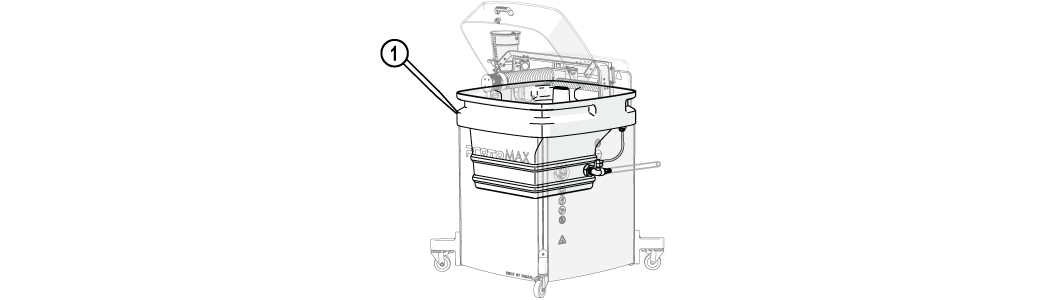
Figure 281
| [1] Catcher tank |
Tank Drain
The adjustable tank drain helps maintain optimal water level by allowing excess water to drain from the catcher tank during cutting operations. The drain has a flexible tube to adjust the water level as needed and allows cutting underwater. The tank overflow allows excess water to exit through the drain port and drain hose to prevent overfilling.
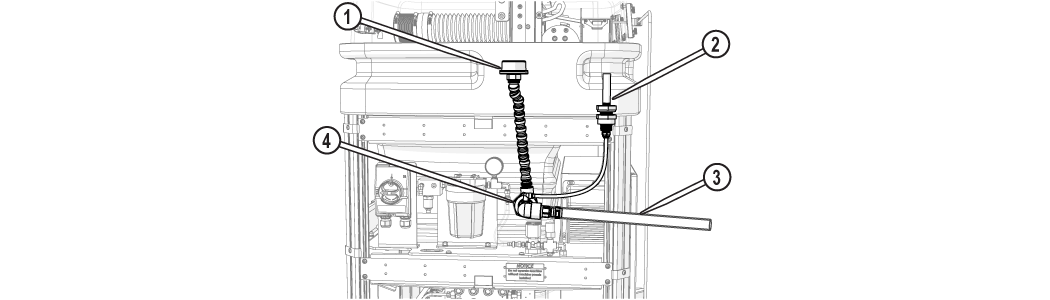
Figure 282
| [1] Adjustable tank drain | [2] Tank overflow drain | [3] Tank drain hose | [4] Tank drain port |
Material Holding System
The material holding system fixtures (secures) materials while machining a part. Fixturing prevents the material from moving, vibrating, floating, tipping, or falling into the tank. The abrasive jet stream is very powerful. The force exerted from the abrasive waterjet stream into the tank can move or float the material during the cutting process. If the material moves during machining, the part will not be precise and may be ruined.
See the help files for best practices tips on fixturing materials.
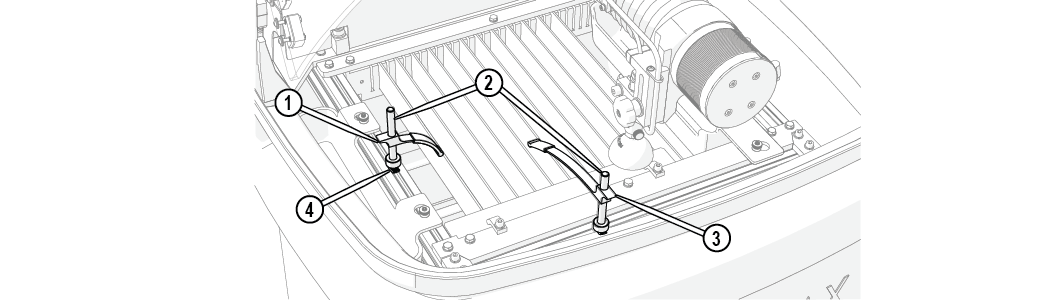
Figure 283
| [1] Holding arm, short | [3] Holding post | [3] Holding arm, long | [4] T-nut |
Power Switch
AC power is controlled by a power switch located on the electrical control enclosure. All ProtoMAX system power is removed when OFF.
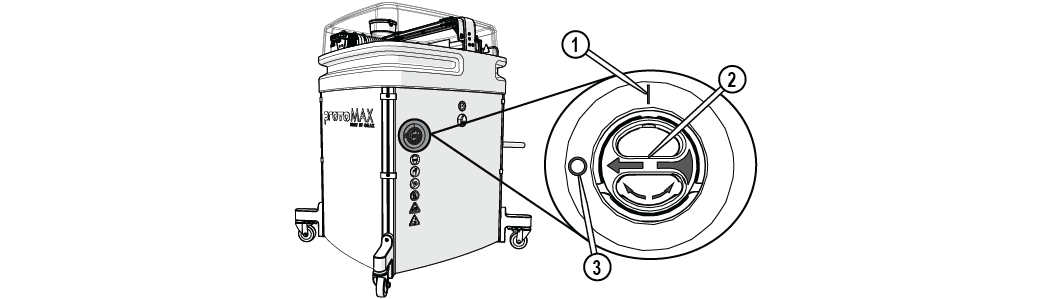
Figure 284
| [1] Power ON position | [2] Power selector | [3] Power OFF position |
Garnet Abrasive Delivery System
The garnet abrasive delivery system consists of the high-pressure nozzle, garnet abrasive feed system (hopper and feed tube), and high-pressure plumbing. The garnet abrasive hopper lid keeps the garnet abrasive from being contaminated with debris or getting wet. The garnet abrasive screen helps to filter small pieces of debris when filling the hopper that may clog the feed tube or nozzle. When machining a part, the garnet abrasive flows from the hopper to the abrasive waterjet nozzle through the garnet abrasive feed tube.
The garnet abrasive material in the hopper must be kept clean and dry. If moisture enters the hopper, the garnet abrasive material will clump and clog the feed tube, which will require cleaning. Even very small particles of dirt will clog the mixing tube. Always store the garnet abrasive material in a covered, dry location protected from metal chips and other debris.
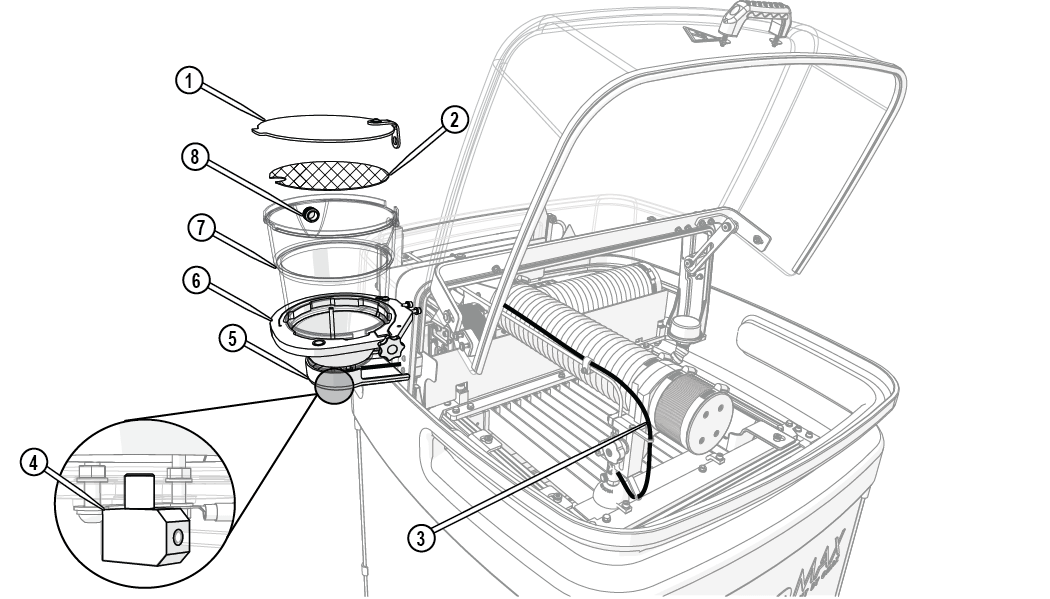
Figure 285
| [1] Hopper lid | [3] Abrasive feed tube* | [5] Hopper splash guard | [7] Garnet abrasive hopper assembly |
| [2] Garnet abrasive screen | [4] Abrasive feed block | [6] Hopper support plate | [8] Bulk abrasive port |
| * tube routing is for illustration purposes only. | |||
Always use garnet abrasive purchased from OMAX. This high-quality abrasive is more consistent in particle size and contain less dust. Inconsistency in particle size makes it difficult to maintain quality when cutting and increases the likelihood of the mixing tube becoming clogged. When dust is present, static electrical charges can build up, causing the garnet abrasive particles to clump together, hindering the garnet abrasive flow.
Abrasive Waterjet Nozzle
The abrasive waterjet nozzle contains a 0.030 in. (0.762 mm) replaceable mixing tube, 0.008 in. (0.2032 mm) replaceable (drop-in) orifice assembly, and nozzle body. High-pressure water is forced through the orifice and enters into a larger mixing chamber, drawing the garnet abrasive from the abrasive feed tube. The water and garnet abrasive is mixed into a high-speed slurry, and then moves into the mixing tube to form the abrasive waterjet stream. The abrasive waterjet stream exits the mixing tube through the bottom of the nozzle to strike and remove the material being machined.
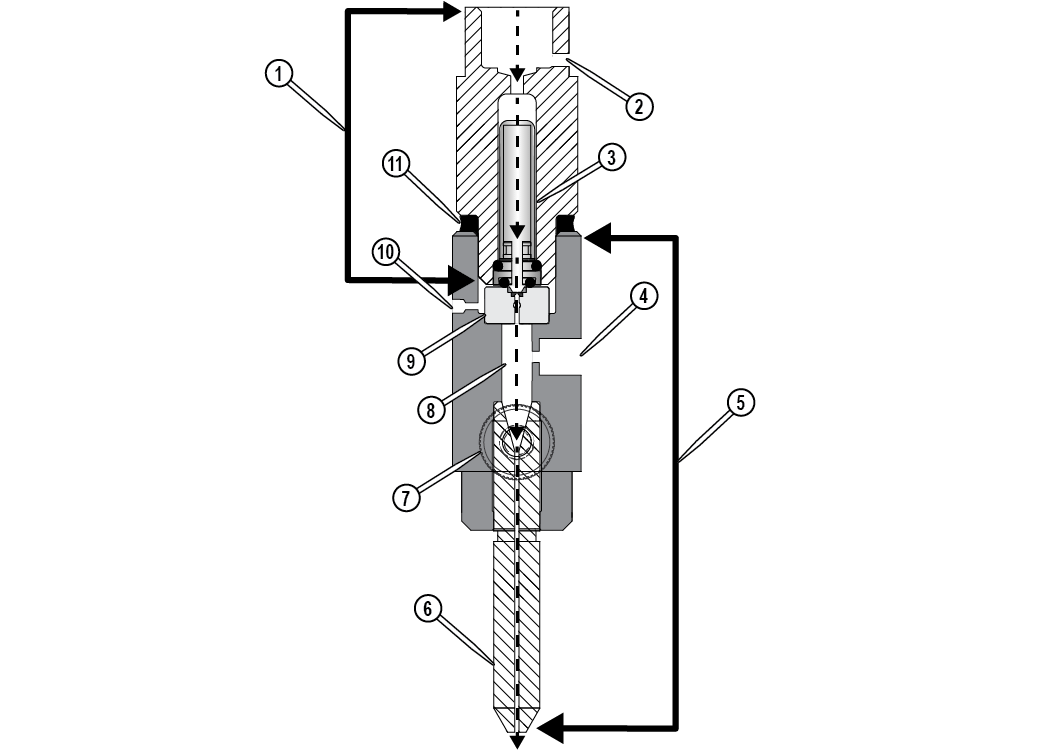
Figure 286
| [1] Nozzle inlet body assembly | [4] Garnet abrasive inlet | [7] Mixing tube retainer | [10] Nozzle body weep hole |
| [2] Inlet body weep hole | [5] Nozzle body assembly | [8] Mixing chamber | [11] Inlet body O-ring |
| [3] Nozzle filter | [6] Mixing tube | [9] Orifice assembly |
High-pressure Pump
The high-pressure pump provides approximately 30,000 pounds per square inch (psi) of cutting pressure for the ProtoMAX. Output high-pressure from the pump is automatically controlled by a variable frequency drive (VFD). The software helps prevent damage to the pump by halting operation when there is inadequate incoming water pressure, excess water temperature, or overpressure events.
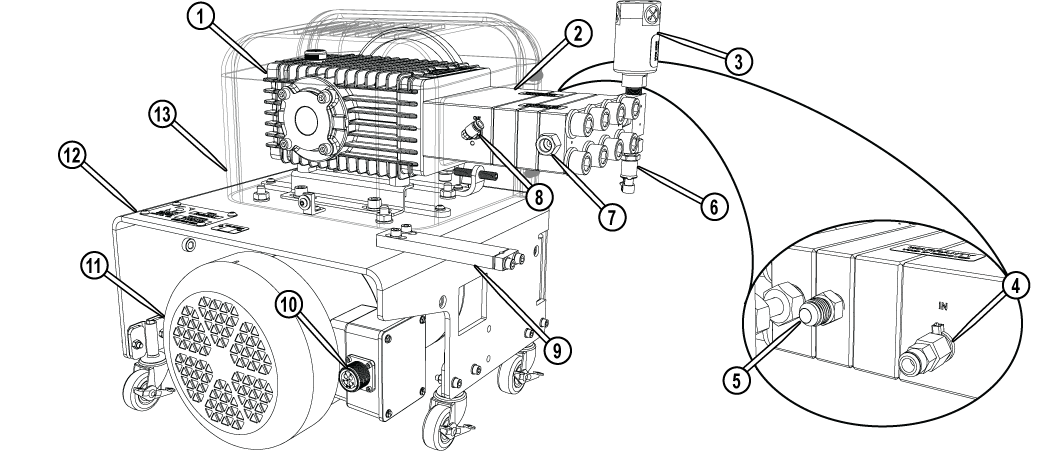
Figure 287
| [1] Crankcase | [6] High-pressure water transducer | [11] Electrical motor |
| [2] High pressure wet-end | [7] High-pressure water OUT connection | [12] Pump frame |
| [3] Safety valve | [8] Cooling line OUT connection | [13] Crankcase cover |
| [4] Cooling line IN connection | [9] High-pressure nipple support bracket | |
| [5] Water IN connection | [10] Electrical connection |
Water Filter
The water filter removes debris from incoming water that can clog and damage the high-pressure components. The water filter is mounted on the side of the table assembly. The outlet water pressure is monitored by the pressure gauge mounted on the water filter.
Do not operate the ProtoMAX without the incoming water supply filter. Operating the ProtoMAX without the water supply filter will introduce debris into the system and may damage the pump and high-pressure system.
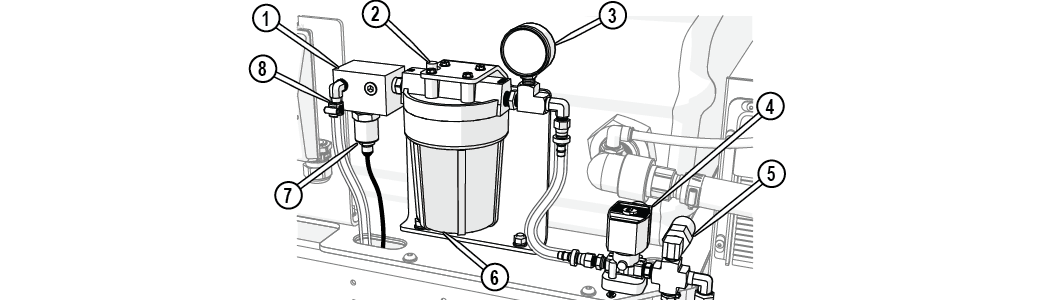
Figure 288
| [1] Water manifold | [4] Water control solenoid | [7] Water temperature transducer |
| [2] Air release button | [5] Water pressure switch | [8] Water connection (incoming) |
| [3] Water pressure gauge | [6] Water filter assembly |
Laptop
The ProtoMAX laptop is pre-installed with Intelli-MAX software and is connected to the ProtoMAX by a USB cable.

Figure 289
Intelli-MAX® Proto Software
Intelli-MAX software by OMAX is easy-to-use and maximizes the functionality of the ProtoMAX Abrasive Waterjet.
LAYOUT is computer aided design (CAD) software that creates tool paths for the ProtoMAX abrasive waterjet system. LAYOUT includes all the basic commands expected in a CAD package, as well as tools specific to abrasive waterjet machining. The LAYOUT help system provides information needed to operate LAYOUT's functions.
MAKE software controls the ProtoMAX abrasive waterjet system by sending precise motor control commands to move the nozzle along a part's cutting path, while controlling the high-pressure water. The MAKE help system provides information needed to operate the software's cutting functions.
See the ProtoMAX Help system for more information on LAYOUT and MAKE.
Accessories
Optional accessories for the ProtoMAX can be found at www.protomax.com.
Make a Part Overview
Intelli-MAX LAYOUT and MAKE are the software tools used in making a part. Following the below listed steps provides the process for successfully making a part. See https://knowledgebase.omax.com for detailed information on making a part.
LAYOUT
| 1. | Import or create a drawing file (DXF file). The first step in making a part is to obtain or create a drawing file. LAYOUT software provides tools to create and edit new and existing drawing files (.dxf) for machining. Drawing files may also be imported from other CAD programs. |
| 2. | Assign machining qualities (edge finish).
The next step is to assign machining qualities (edge finish) to the drawing entities (lines, arcs, etc.) that tell the nozzle how fast or slow to move to obtain the desired edge finish. |
| 3. | Clean the drawing.
Next, the drawing should be cleaned to remove duplicate entities, extra dots, gaps, and other garbage entities that are hard to find in the drawing. A clean drawing eliminates machining confusion by defining only one continuous path for the machine to follow. |
| 4. | Add path elements to the drawing.
After cleaning, path elements need to be drawn. Path elements tell the machine where to cut, where to travel without cutting (traverse), when to pierce the material (lead in) and the exit points (lead out). |
| 5. | Create the machine tool path file (ORD/OMX).
The last step in LAYOUT is to convert the drawing file to a machine tool path file (ORD/OMX) that tells the machine how to cut the part. |
MAKE
| 6. | Start up the machine.
After the drawing file is prepared and converted to a machine tool path file, the next step is to start the machine per the Startup Checklist. |
| 7. | Open and configure the ORD/OMX file.
The tool path file is opened and the material setup data is entered so the machine knows the path to cut and the material type and thickness. |
| 8. | Load and secure the material.
The material is then placed and secured to the cutting stage. Fixturing the material to prevent any movement in the X, Y, or Z directions is critical in making good parts. |
| 9. | Position the nozzle
Attach the splash guard to the nozzle assembly with the cup up. Set the nozzle stand-off at the highest point of the material surface, then move the nozzle to the start of the machine tool path. |
| 10. | Prepare for machining.
Conduct a dry run to ensure the part fits on the material and the nozzle clears any obstacle. Any problems found during the dry run can be corrected before machining the part. |
| 11. | Machine the part.
Flip the splash guard cup down. Adjust the drain, then add water to raise it above the material surface (if applicable), then begin machining. When finished remove and inspect the part. |
Operate the ProtoMAX
See the Intelli-MAX® Help system for additional information on using LAYOUT and MAKE software.
Startup Checklist
The following checklist is a quick reference to ensure equipment startup tasks are completed in the required sequence. Detailed instructions are located in Start the ProtoMAX.
| Turn ON the laptop (do not open the MAKE application) | |
| Connect the USB cable to the laptop | |
| Turn ON the main power; verify the light comes on | |
| Turn ON the water supply | |
| Check the water pressure | |
| Open the MAKE application | |
| Home the machine | |
| Conduct a nozzle test without abrasive | |
| Fill the hopper with garnet abrasive | |
| Conduct a nozzle test with abrasive | |
| Verify the garnet abrasive is flowing from the hopper to the nozzle | |
| Inspect the visible high-pressure plumbing connections for leaks | |
| Open and configure a kerf check sample file or the part to cut | |
| Load and secure the material on the cutting stage | |
| Set the nozzle stand-off | |
| Position the nozzle at path start point | |
| Perform a dry run | |
| Fold down the splash guard cup | |
| Add water to raise the water level above the material surface, adjust the drain height if needed | |
| Begin machining the part | |
| Check the cutting water pressure | |
| Adjust the tool offset if needed |
A kerf check is performed only to verify mixing tube wear and to adjust the tool offset if needed.
Start the ProtoMAX
| 1. | Turn ON the laptop power. |
Do not open MAKE. The ProtoMAX USB cable must be plugged in and recognized by the laptop before opening the MAKE program.
| 2. | Connect the ProtoMAX USB cable [1] to the laptop. |
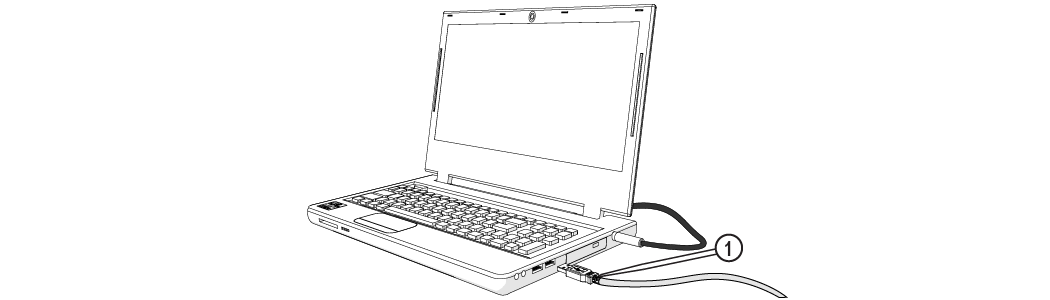
Figure 290
| 3. | Turn ON the main power [2] and verify the light [1] is on. |
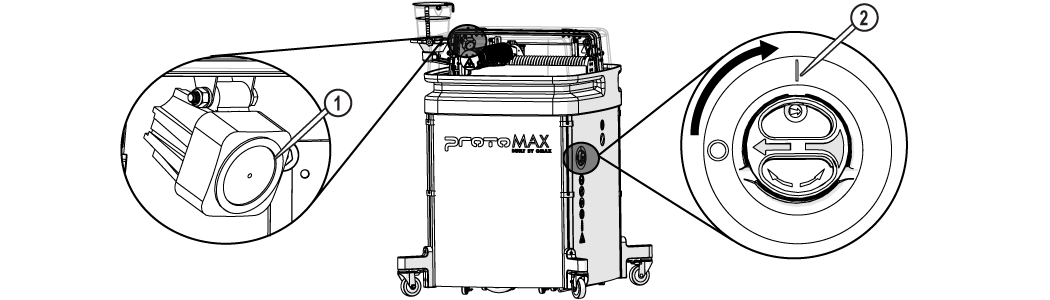
Figure 291
| 4. | Turn ON the incoming water supply. |
| 5. | Record the incoming water pressure (Figure 292). |
The incoming water pressure should be 45–85 psi.
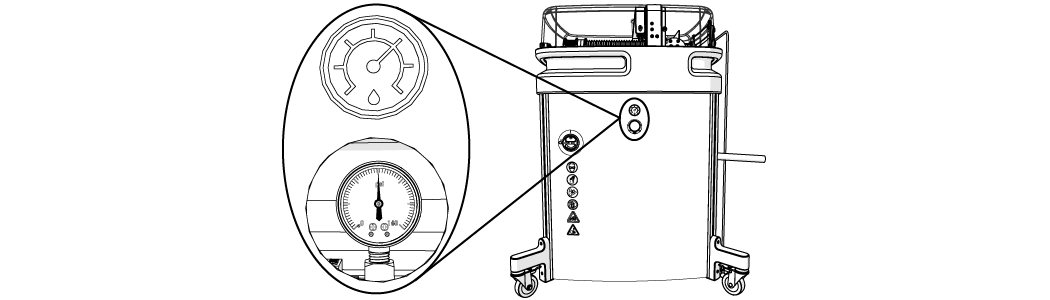
| 6. | Open the software. |
| 7. | Click the to home the machine. |
Home is required after every power cycle. For example, when the main power switch is turned OFF and then turned back ON, during power outages, or the main power cord is disconnected.

Figure 293
| 8. | Conduct a nozzle test without abrasive. |
| a. | Open and secure the lid. |
Use care when opening or closing the lid to avoid injury. Keep hand, fingers, or body part away from the side of the table when closing the lid. Never let the lid free-fall.
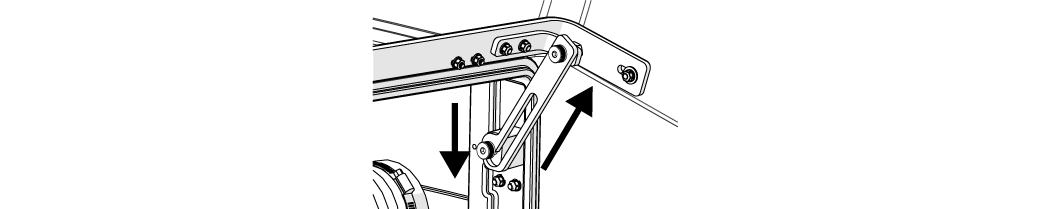
Figure 294
| b. | Remove the abrasive feed tube from the nozzle and place it over the top of the Y-axis [1]. |
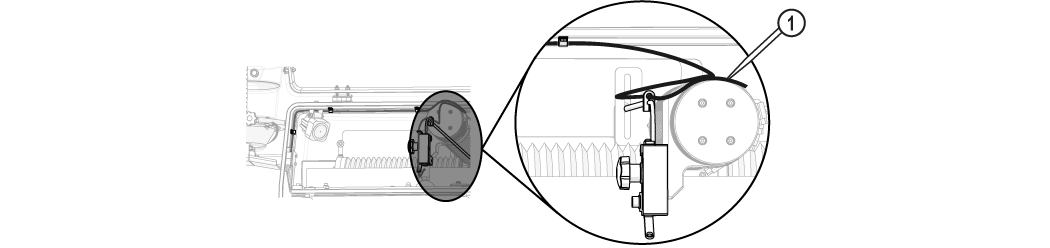
Figure 295
| c. | Verify the mixing tube is properly seated and secured in the nozzle body. |
Figure 296
| d. | Place the nozzle splash guard [1] on the mixing tube [2] with the cup folded up. |
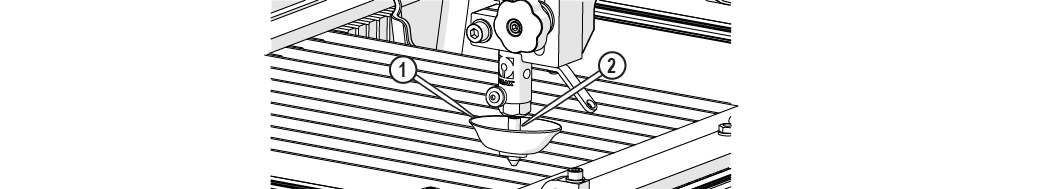
Figure 297
| e. | Position the nozzle in the center of the tank, between two slats using the , buttons or keyboard arrow keys. |
Figure 298
| f. | Lower the nozzle to within 1 in. of the surface of the water. |
Always hold the nozzle when loosening the hand knob. Do not let the nozzle fall and strike the cutting deck slats or material to avoid damage to the nozzle and/or nozzle components.
| g. | Close the lid. |
| h. | Click [1]. |
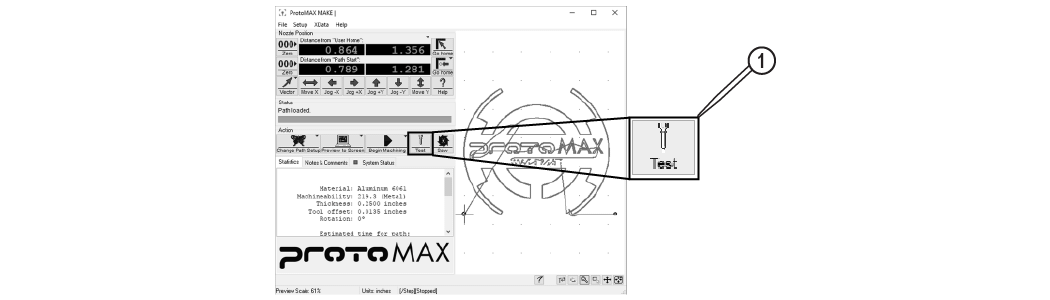
Figure 299
| i. | In Test Operations, select Test Cutting Head (Pump, Jet, and Abrasive), and click . |
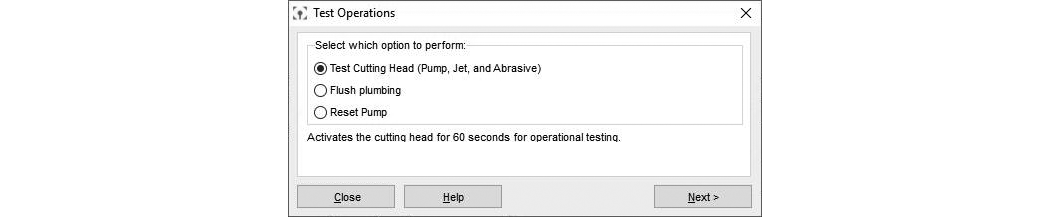
Figure 300
| j. | Click . |
Figure 301
| k. | Click when the test is complete. |
| 9. | Fill the hopper with garnet abrasive. |
| a. | Remove the hopper lid. |
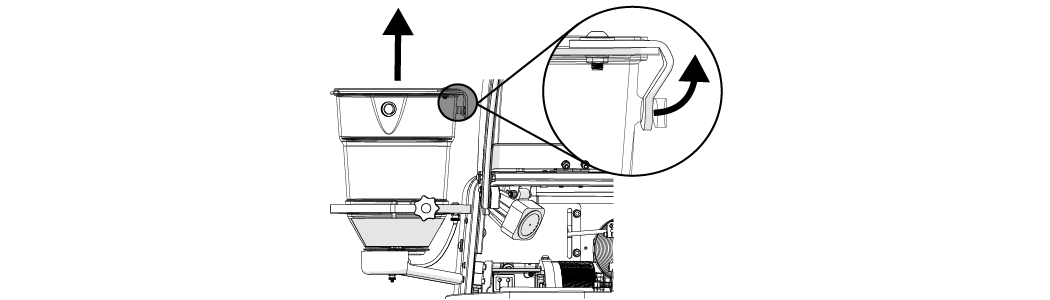
Figure 302
| b. | Pour the garnet abrasive through the garnet abrasive screen into the hopper. |
Gently tap the hopper side to evenly settle the garnet abrasive in the hopper.
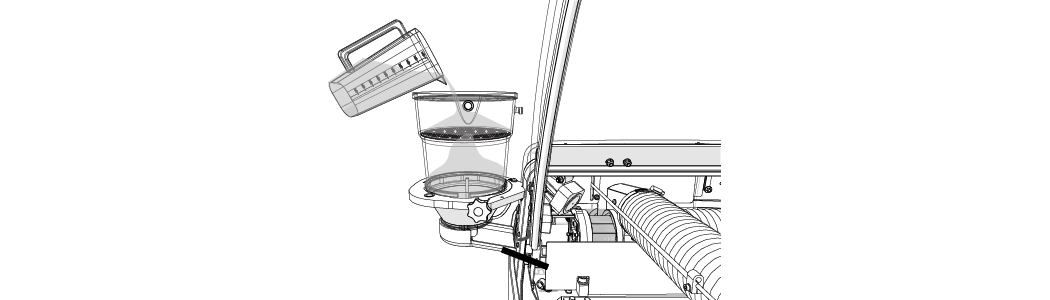
Figure 303
| a. | Replace the hopper lid. |
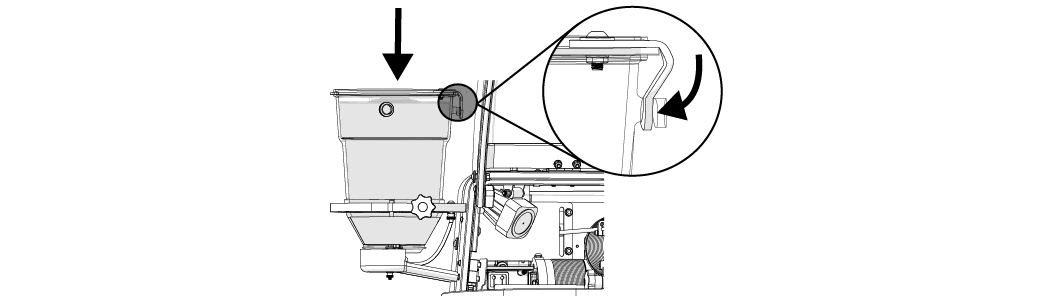
Figure 304
| 10. | Conduct a nozzle test with abrasive. |
Use care when opening or closing the lid to avoid injury. Keep hand, fingers, or body part away from the side of the table when closing the lid. Never let the lid free-fall.
| a. | Open the lid. |
| b. | Visually check the condition of the garnet abrasive feed tube, replace as needed. |
| c. | Connect one end of the garnet abrasive feed tube to the garnet abrasive feed block [1] and connect the other end to the nozzle [2]. |
Bacteria in the tank water can build up. A minor break in the skin can introduce harmful bacteria into a wound. Always wear protective gloves if you have cuts or open wounds on your hands. When setting up material for cutting, wear gloves that provide protection against sharp metal edges.
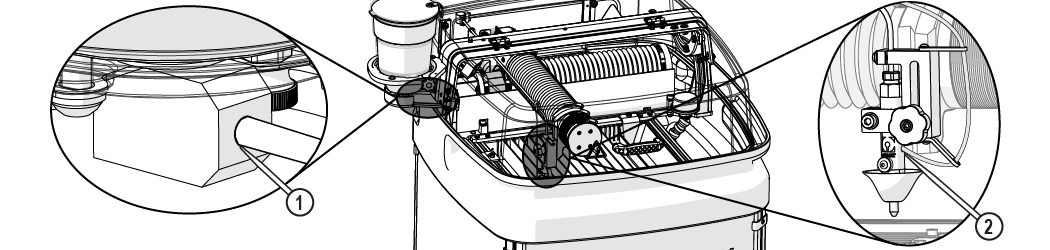
Figure 305
| d. | Open and use the , buttons [1] or keyboard arrow keys to position the nozzle between two slats. |
Figure 306
| e. | Lower the nozzle to within 1 in. (3 cm) of the surface of the water, if needed. |
Always hold the nozzle when loosening the hand knob. Do not let the nozzle fall and strike the cutting deck slats or material to avoid damage to the nozzle and/or nozzle components.
| f. | Click Test [1]. |

Figure 307
| g. | In Test Operations, select Test Cutting Head (Pump, Jet, and Abrasive), and click . |

Figure 308
| h. | Click . |

Figure 309
| 11. | Observe the garnet abrasive tube [1] at the hopper to verify the garnet abrasive is flowing, then click when the test is complete (Figure 310). |
The garnet abrasive flow is fast and hard to see. The sound increases indicating garnet abrasive is flowing.
| 12. | Inspect the nozzle [1] and all visible high-pressure plumbing [2] connections for leaks. |
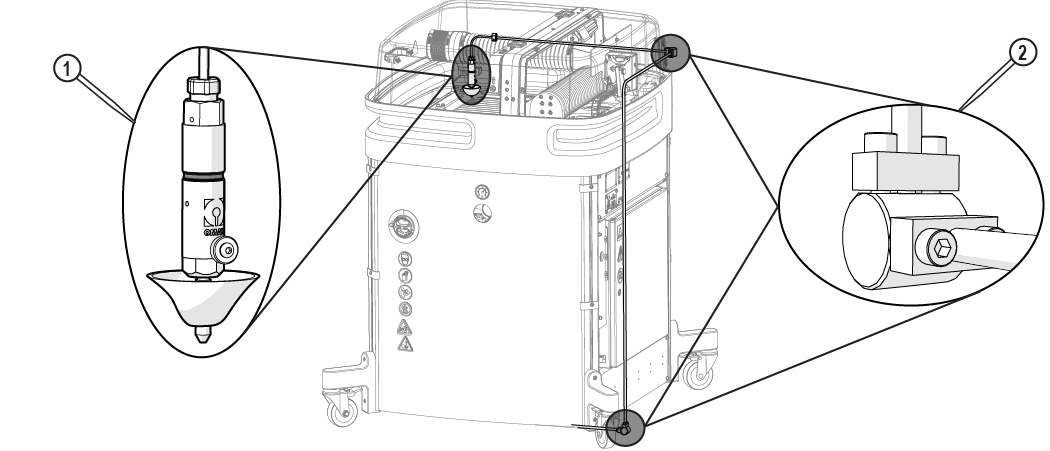
Figure 311
| 13. | Open and configure the kerf check sample file. |
 Cutting Best Practices and How to Cut the Kerf Check Part
Cutting Best Practices and How to Cut the Kerf Check Part
| a. | In MAKE, open and configure the kerf check sample file. |
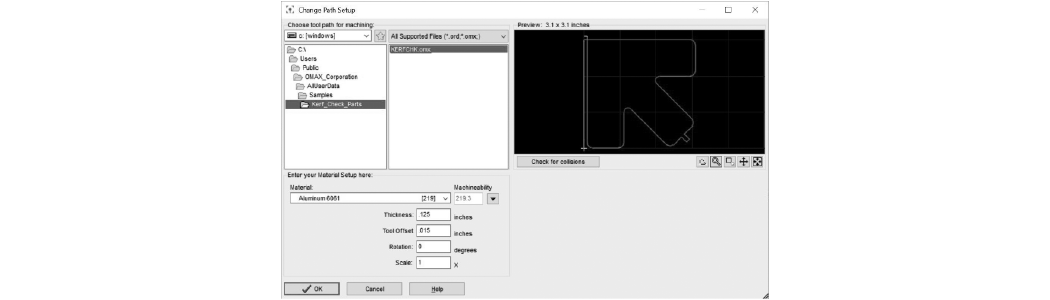
Figure 312
| b. | Open and secure the lid. |
Use care when opening or closing the lid to avoid injury. Keep hand, fingers, or body part away from the side of the table when closing the lid. Never let the lid free-fall.

Figure 313
Bacteria in the tank water can build up. A minor break in the skin can introduce harmful bacteria into a wound. Always wear protective gloves if you have cuts or open wounds on your hands. When setting up material for cutting, wear gloves that provide protection against sharp metal edges.
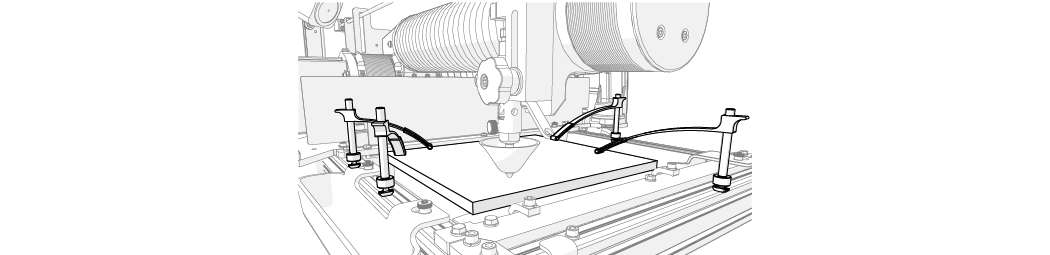
| 14. | Load and secure the material on the cutting stage. |
| 15. | Set the nozzle standoff at the highest point on the material. |
Always hold the nozzle when loosening the hand knob. Do not let the nozzle fall and strike the cutting deck slats or material to avoid damage to the nozzle and/or nozzle components.
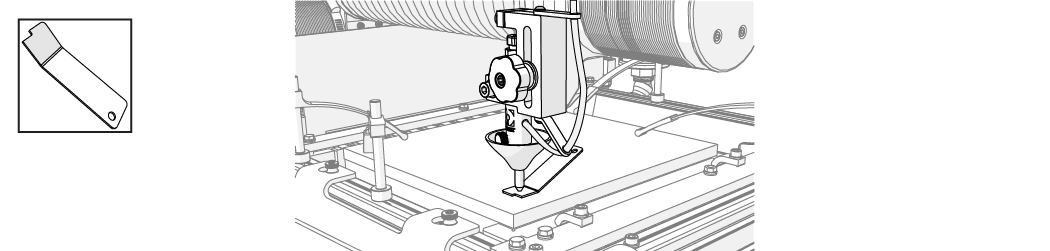
Figure 315
| 16. | Position the nozzle at the path start. |
To extend the life of the catcher tank, cut towards the center of the tank. Continuous cutting at the outer edges of the cutting envelop may allow the jet stream to wear through the sides of the catcher tank.
| 17. | Close the lid. |
Use care when opening or closing the lid to avoid injury. Keep hand, fingers, or body part away from the side of the table when closing the lid. Never let the lid free-fall.
| a. | Lift the lid and push the support arm towards the back. |
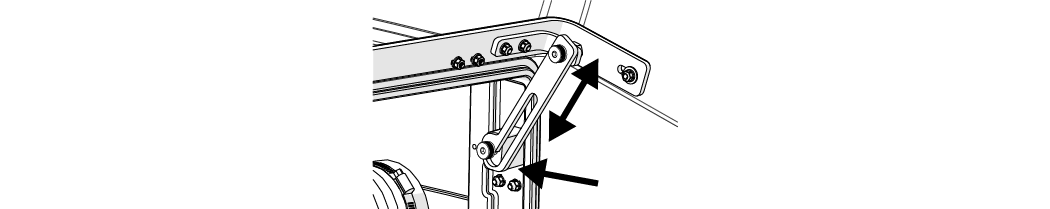
Figure 316
| b. | Lower the lid to the catcher tank. |
| 18. | Perform a dry run. |
| a) | Open and configure (set the material type and thickness) for the machine tool path for the part. |

Figure 317
| b) | Click Go home [1] to move the nozzle to the Path Start Home position, if needed. |
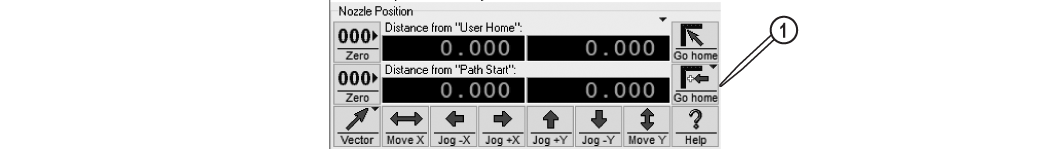
Figure 318
| c) | Click to display the Path Control dialog box. |

Figure 319
| d) | Right-click the button to display a list of dry run options. |
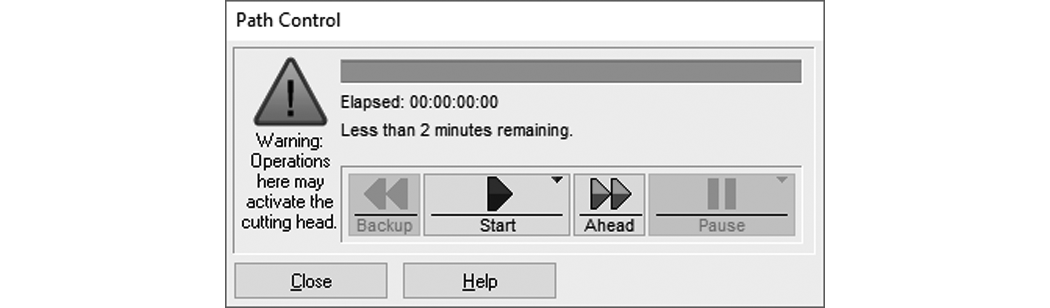
Figure 320
| e) | Click . |
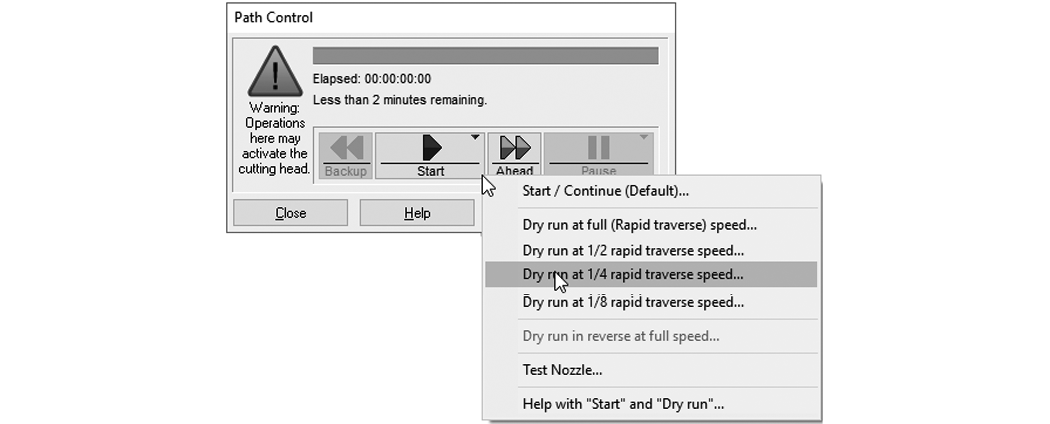
Figure 321
| f) | At any time, click if potential problems are seen during the dry run process to stop nozzle movement. |

Figure 322
| g) | When the dry run is finished, click the button to close the Path Control dialog. |

Figure 323
| 19. | Click in the Path Start dialog box to move the nozzle to the path start point. |
| 20. | Fold down splash guard cup. |
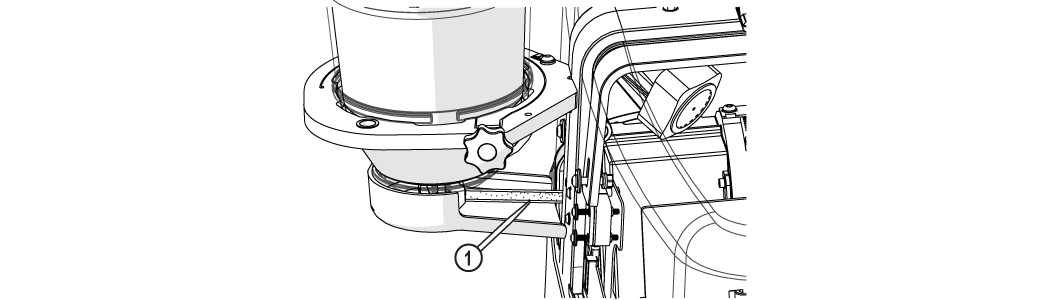
| 21. | Adjust the tank drain [1] and fill the tank with water above the material (if possible). |
To extend the life of the catcher tank, cut towards the center of the tank. Continuous cutting at the outer edges of the cutting envelop may allow the jet stream to wear through the sides of the catcher tank.
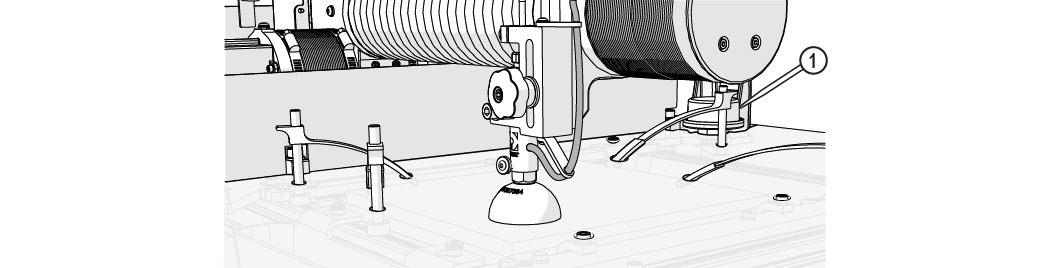
Figure 324
Cut parts under water when possible. Cutting under water lowers the noise level and reduces the mist and splash created by the water and abrasive. Cutting under water also helps the garnet bins collect cutting debris instead allowing the debris to settle in the tank, which makes tank cleaning easier.
| 22. | Close the lid. |
| 23. | Cut the part. |
| a. | Click Begin Machining [1]. |
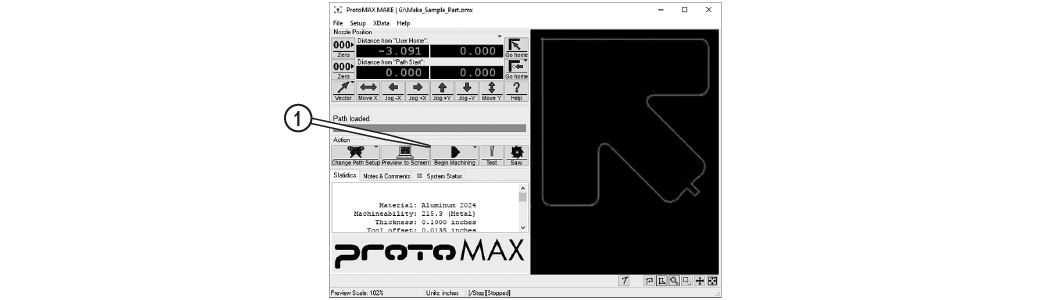
Figure 325
| b. | Click . |

Figure 326
| 24. | Check the cutting water pressure and compare to the recorded incoming water pressure. |
If the cutting water pressure is 25 psi or lower, the water filter should be changed (see 401440-EN Maintenance, ProtoMAX).
| 25. | Adjust the tool offset [1] if needed, see Measuring the Abrasivejet Kerf.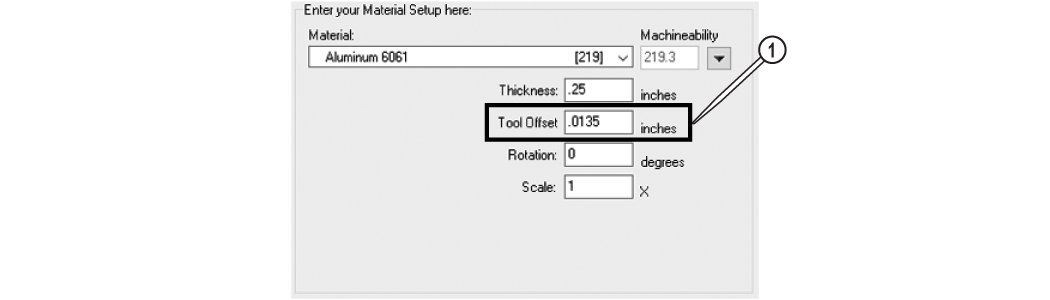 |
Figure 327
Shutdown Checklist
The following checklist is a quick reference to ensure equipment shutdown tasks are completed in the required sequence. Detailed instructions are located in Shutdown the ProtoMAX.

| Position the nozzle for shutdown | |
| Remove the abrasive feed tube from the nozzle | |
| Run test nozzle to clear the nozzle | |
| Close MAKE | |
| Turn OFF the laptop | |
| Turn OFF the ProtoMAX | |
| Clean the machine | |
| Turn OFF the water supply | |
| Turn OFF the breaker power switch, if needed |
Shutdown the ProtoMAX
| 1. | Conduct a nozzle flush. |
| a. | Open the lid. |
Use care when opening or closing the lid to avoid injury. Keep hand, fingers, or body part away from the side of the table when closing the lid. Never let the lid free-fall.

Figure 328
| b. | Remove the garnet abrasive tube [1] from the nozzle and place it over the Y-axis. |

Figure 329
| c. | Close the lid. |
Use care when opening or closing the lid to avoid injury. Keep hand, fingers, or body part away from the side of the table when closing the lid. Never let the lid free-fall.
| d. | Open MAKE and use the X, buttons [1] or keyboard arrow keys to position the nozzle in the center of the tank between two slats. |

Figure 330
| e. | Click Test [1]. |

Figure 331
| f. | In Test Operations, select Test Cutting Head (Pump, Jet, and Abrasive), and click . |

Figure 332
| g. | Click . |

Figure 333
| h. | Click . |

Figure 334
| i. | Verify there is no moisture or debris in the abrasive feed tube. |
| j. | Insert the garnet abrasive tube into the nozzle. |
Figure 335
| k. | Close the software. |
| 2. | Turn OFF the laptop. |
| 3. | Clean the machine with a clean, damp cloth. |

Never spray water on the electrical control cabinet or exterior surfaces of the machine. Water may enter the electrical control cabinet and damage internal components.
| a. | Remove any cutting debris from the cutting stage. |
| b. | Remove any cutting debris from the axes bellows. |
| c. | Remove any cutting debris from the lid. |
| d. | Close the lid. |
| e. | Wipe down the exterior surfaces of the machine. |
Use care when opening or closing the lid to avoid injury. Keep hand, fingers, or body part away from the side of the table when closing the lid. Never let the lid free-fall.
| 4. | Turn OFF [1] the ProtoMAX. |
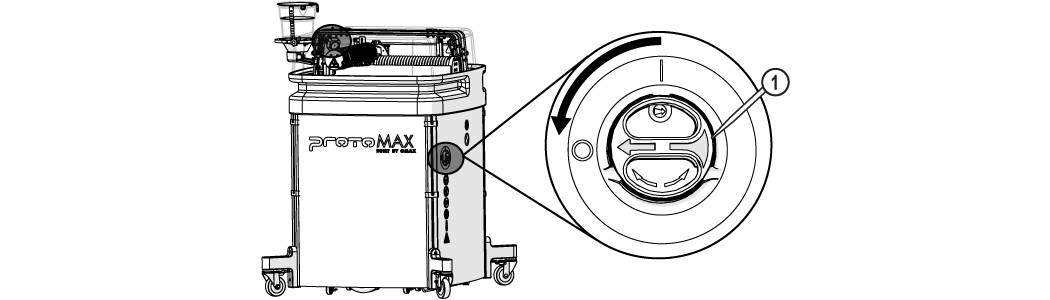
Figure 336
| 5. | Turn OFF the water. |
| 6. | Turn OFF the breaker power switch, if needed. |
Cut the Fixturing Square
See the fixturing-square instructions and video for additional information on cutting the fixturing square.
A fixturing square [1] establishes an X and Y reference to a known point in the cutting deck. The square provides a stable base for securing parts for cutting, and assists in maximizing material use when cutting. It can be used to precisely locate features on existing parts, or as a convenient surface to secure material against when cutting.
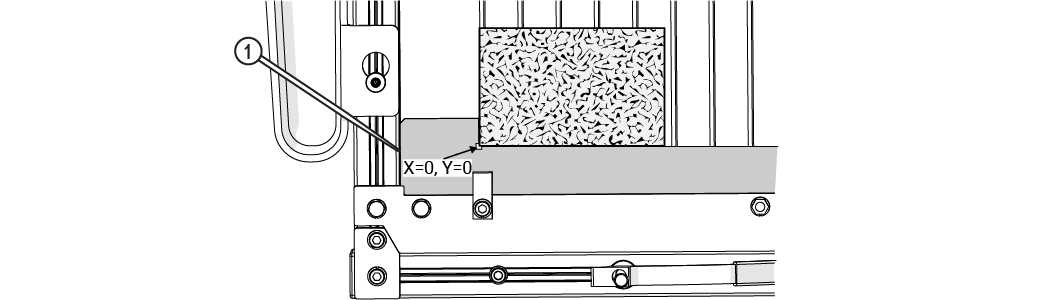
Figure 337
A square fixture is made by clamping material along the X-front frame in the machine cutting deck, and then using the machine to cut an "L" shape into it. Since the machine cuts the "L," we know it to be true and square to the machine's X- and Y-axes.
Recover from a Nozzle Clog
There are multiple scenarios resulting from a clog in the nozzle. The fix depends on how far water has traveled back up the abrasive feed tube and whether the water entered the abrasive hopper or not. In all scenarios, correct the condition that caused the nozzle to clog, such as wet garnet, a blocked orifice, a blocked mixing tube, or other before continuing operation.
| 1. | Remove the garnet abrasive feed tube from the nozzle assembly [2] and the garnet abrasive feed block [1]. |

Figure 338
| 2. | Use clean, dry air to completely clear the clog from the abrasive feed tube. |
If the water entered the abrasive feed block:
| 3. | Remove the hopper splash guard. |
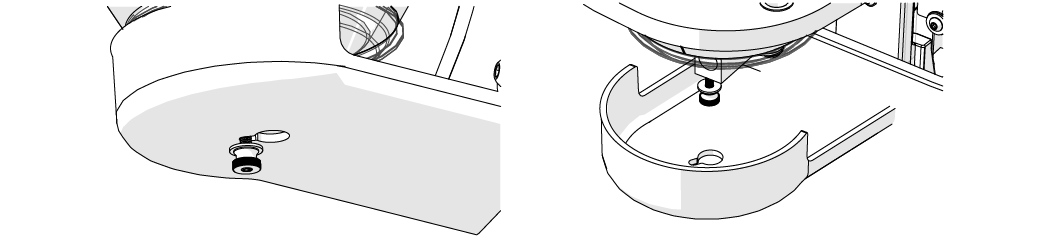
Figure 339
| 4. | Remove the hopper ground strap [1]. |
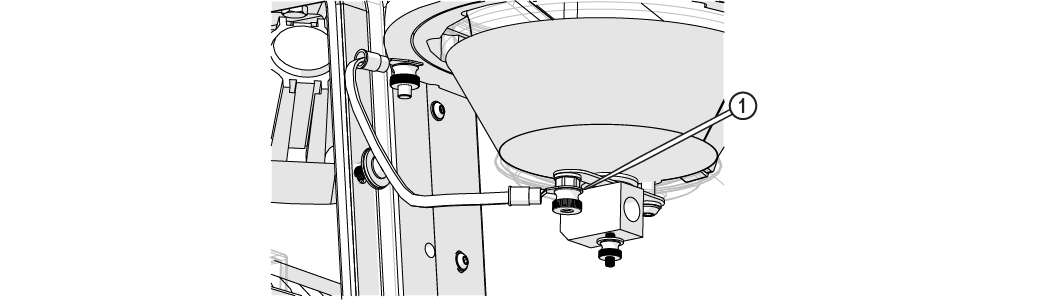
Figure 340
| 5. | Remove the abrasive feed block [2] and insert the red plug [1] to prevent garnet from pouring out from the bottom of the hopper assembly. |
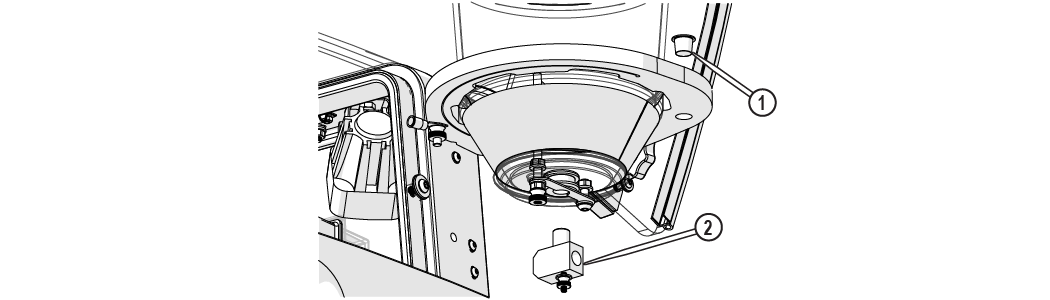
Figure 341
| 6. | Use clean, dry air to completely blow out all debris, clumps, or clogs from the abrasive feed block. |
If the water entered the hopper assembly:
| 7. | Loosen the knob [1] and remove the hopper assembly from the hopper support plate. |
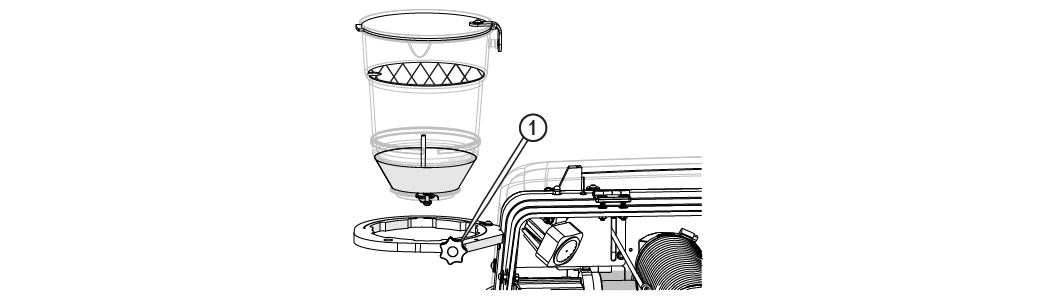
Figure 342
| 8. | Completely empty and wipe out the hopper. |
Make sure the hopper container is completely dry prior to filling with dry garnet abrasive. Do not reuse garnet abrasive. The hopper screen may not sufficiently remove moist clumps from the wet abrasive. Garnet that has been exposed to moisture will clump and cannot be reused. Garnet that has been exposed to moisture will result in additional clogging.
| 9. | Raise the Z-axis. |
| 10. | Remove the nozzle splash guard and mixing tube [1] from the nozzle body. |
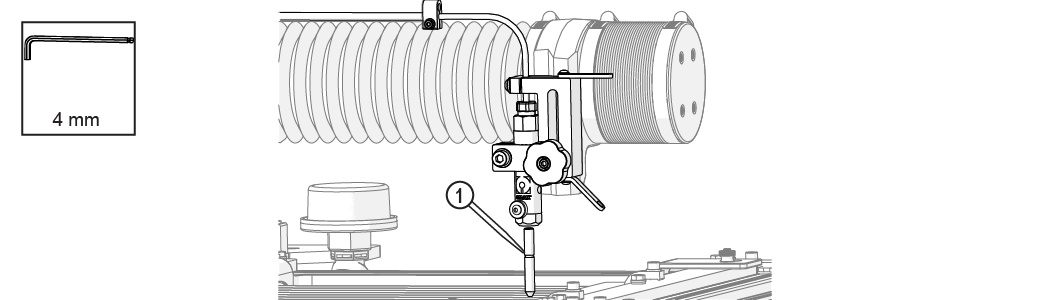
Figure 343
| 11. | Inspect the mixing tube to see if light is visible through the bore. |
If light is visible:
| 12. | Re-install the mixing tube [1] into the nozzle body. |
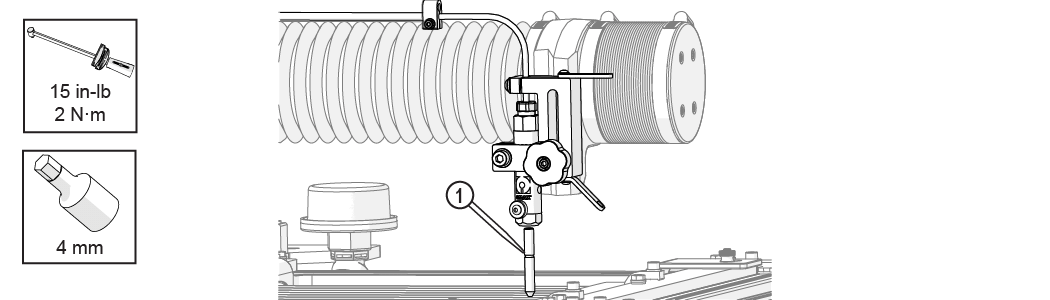
Figure 344
If light is not visible:
| 13. | Turn the mixing tube [1] upside down and insert it back into the nozzle body and tighten it. |
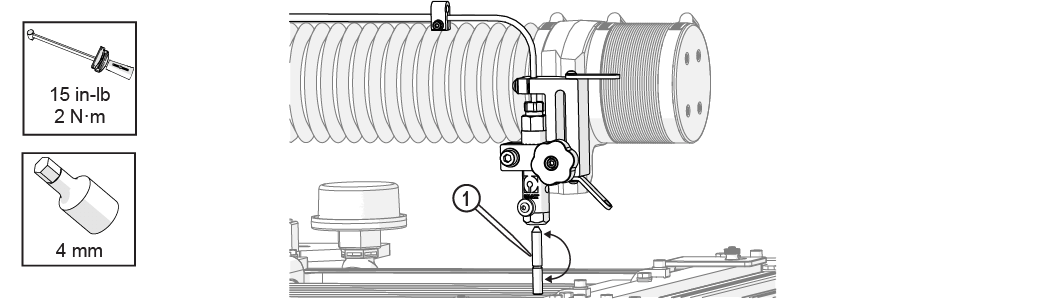
Figure 345
| 14. | Position the nozzle towards the center of the tank (off the material) between two slats. |
| 15. | Lower the Z-axis to approximately 1 in. (3 cm) above the water surface. |
| 16. | Close the lid. |
Use care when opening or closing the lid to avoid injury. Keep hand, fingers, or body part away from the side of the table when closing the lid. Never let the lid free-fall.
| 17. | Open the dialog box and run a nozzle test to clear the mixing tube. |
| 18. | Remove the mixing tube [1]. |

Figure 346
| 19. | Remove the nozzle body assembly from the nozzle inlet body. |
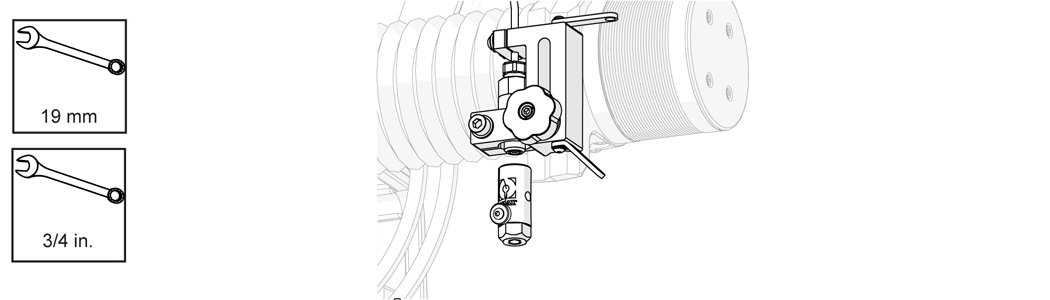
| 20. | Remove the orifice assembly [1] and inspect the chamber bore [2]. |
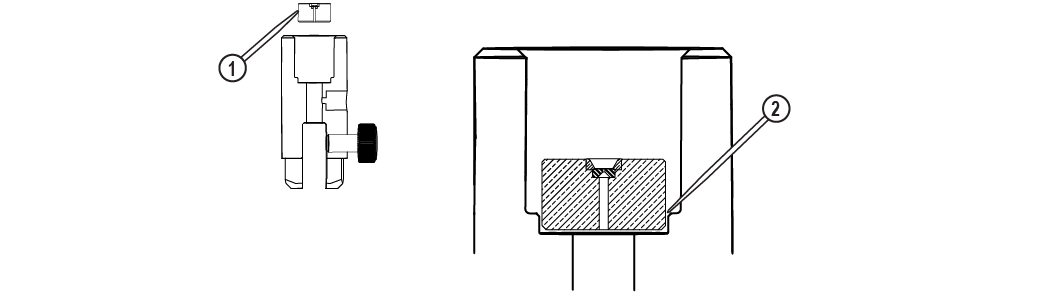
Figure 348
| 21. | Clean the orifice assembly and the nozzle body (including the air vent hole) thoroughly prior to reassembly. |
Do not use a brush or cotton swab or foam-tipped applicator to apply lubricants because they may leave fibers and plug the nozzle.
| 1. | Clean the inlet body threads by wiping with a clean rag. |
| 2. | Apply a light coat of Blue Goop to the second and third threads [1] of the inlet body, then spread the lubricant evenly around the inlet body threads. |
Use care when applying lubricants around high-pressure water routes. Lubricants can enter the high-pressure water system and clog the orifice and/or mixing tube.
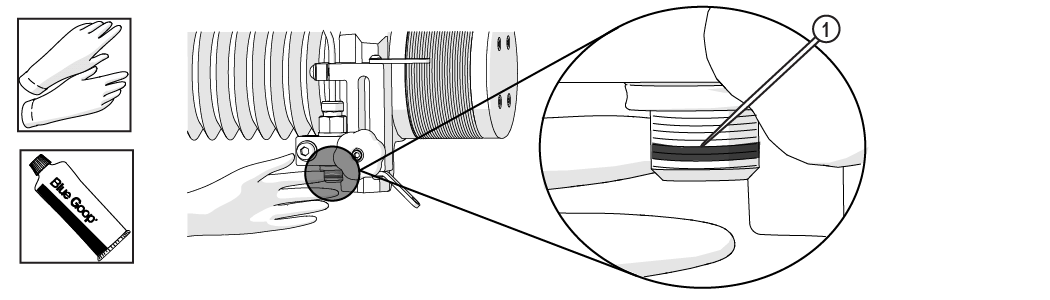
Figure 349
| 3. | Wipe the excess Blue Goop from the end of the inlet body [1]. |
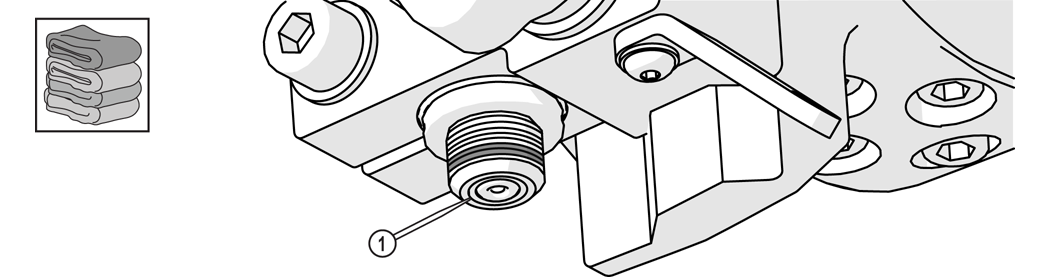
Figure 350
| 4. | Apply a light coat of Blue Goop to the first and second nozzle body threads [1], then spread the lubricant evenly around the nozzle body threads. |
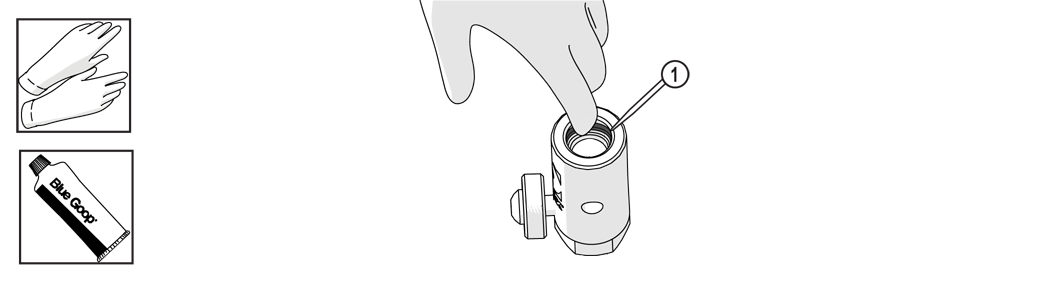
Figure 351
| 5. | Wipe the excess Blue Goop from the end of the nozzle body [1]. |
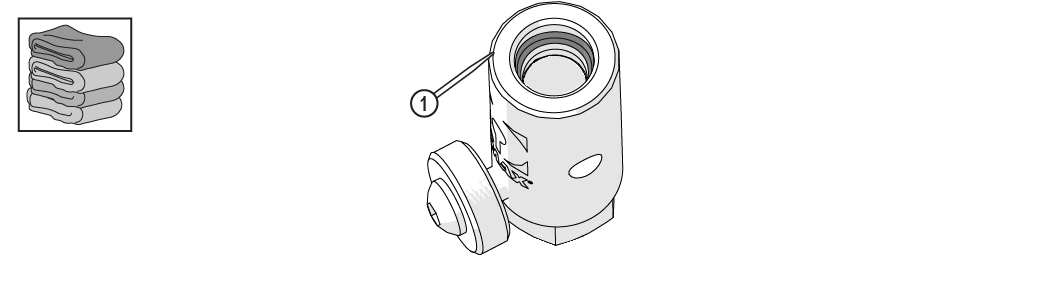
Figure 352
Once the nozzle is completely clean:
Always orient the orifice assembly so the brass [1] is visible from the top of the nozzle body. Inserting the orifice assembly in nozzle body in the incorrect orientation [2] may cause damage to the orifice assembly.
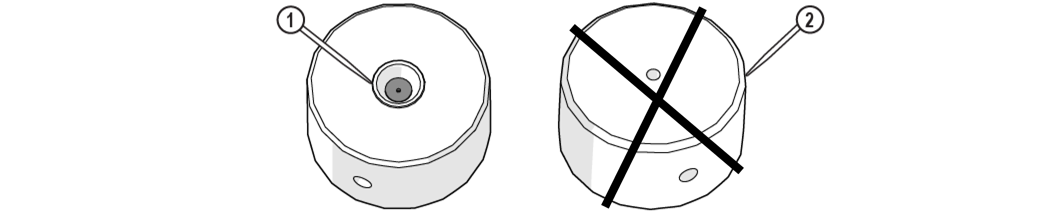
Figure 353
| 6. | Insert the orifice assembly [1] into the nozzle body and adjust the orifice to ensure the it is seated correctly in the chamber bore [2]. |

| 7. | Re-install the nozzle assembly on the nozzle inlet body. |
| 8. | Raise Z-axis and move the cutting head over the material. |
| 9. | Insert and the mixing tube. |
| 10. | Close the Path Control window. |
| 11. | Re-install the hopper and its components (abrasive feed block, feed tube, ground strap, and hopper splash guard. |
When installing the abrasive hopper, ensure the washer is located on the underside of the hopper splash guard.
| 12. | Fill the hopper with fresh, dry abrasive. |
| 13. | Connect the abrasive tube to the nozzle body. |
If an alert or fault message is displayed, reset the pump (see Reset the Pump).
| 14. | Attach the nozzle splash guard. |
| 15. | Set the nozzle stand-off. |
| 16. | Close the lid. |
Use care when opening or closing the lid to avoid injury. Keep hand, fingers, or body part away from the side of the table when closing the lid. Never let the lid free-fall.
To continue cutting the part, using MAKE:
| 17. | Click in the Path Start Home dialogue. |
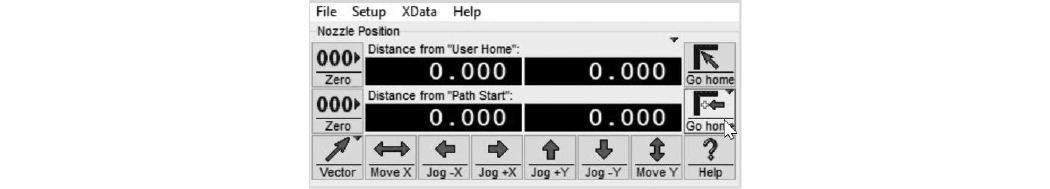
Figure 356
| 18. | Right-click . |

Figure 357
| 19. | Click . |
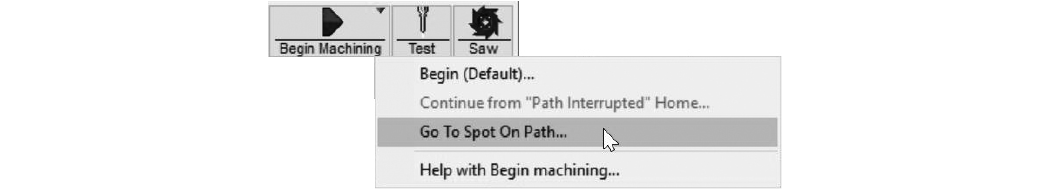
Figure 358
| 20. | Move the cursor over the spot on the tool path slightly before the clog occurred and left click. |
| 21. | Click on Machine will now traverse into position dialog box. |
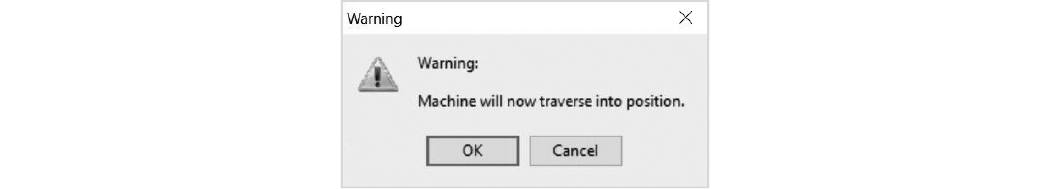
Figure 359
| 22. | Click to start cutting. |
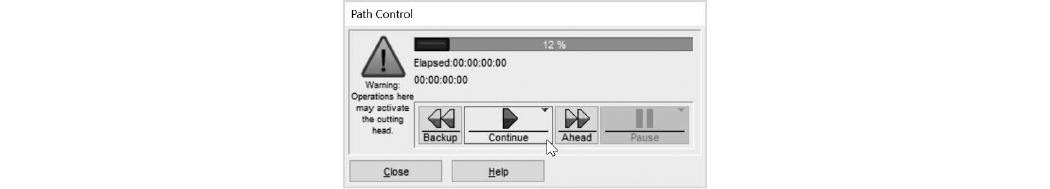
Figure 360
If nozzle clogging continues, it may be necessary to replace the abrasive feed tube, the mixing tube, nozzle orifice, and/or nozzle filter as one or more of these components may be causing the problem.
Reset the Pump
The reset pump test runs a 30 second sequence to reset the pump. This test should be done before operating the ProtoMAX for the first time, after changing the nozzle orifice, repairing or replacing the pump, repairing any high pressure plumbing leaks, or when required by a fault or alert message.
| 1. | Open MAKE. |
| 2. | Move the nozzle between two slats. |
| 3. | Click . |
| 4. | In Test Operations, select Reset Pump, and click . |
| 5. | Click and check the high-pressure plumbing for leaks (the dialog box closes when the test is complete). |
Technical Support
Refer to the ProtoMAX website for technical support contact information.
Warranty
Contact Customer Support or go to the ProtoMAX website.